PDC vs matrix/carbon bits: best uses by formation?
Selecting the appropriate drill bit type significantly impacts operational efficiency, cost management, and project success across industrial drilling applications. The choice between PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) bits and matrix/carbon bits depends heavily on geological formation characteristics, drilling objectives, and project-specific requirements. PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling technology represents a revolutionary advancement in drilling efficiency, offering superior performance in various formation types. Matrix and carbon bits provide alternative solutions with distinct advantages in specific drilling scenarios. Understanding the optimal application of each bit type based on formation characteristics enables procurement professionals and technical engineers to make informed decisions that maximize drilling performance while minimizing operational costs. This comprehensive comparison examines the fundamental differences, performance metrics, and strategic applications of these critical drilling technologies.
Understanding PDC and Matrix/Carbon Bits: Composition and Mechanism
PDC Bit Construction and Operation
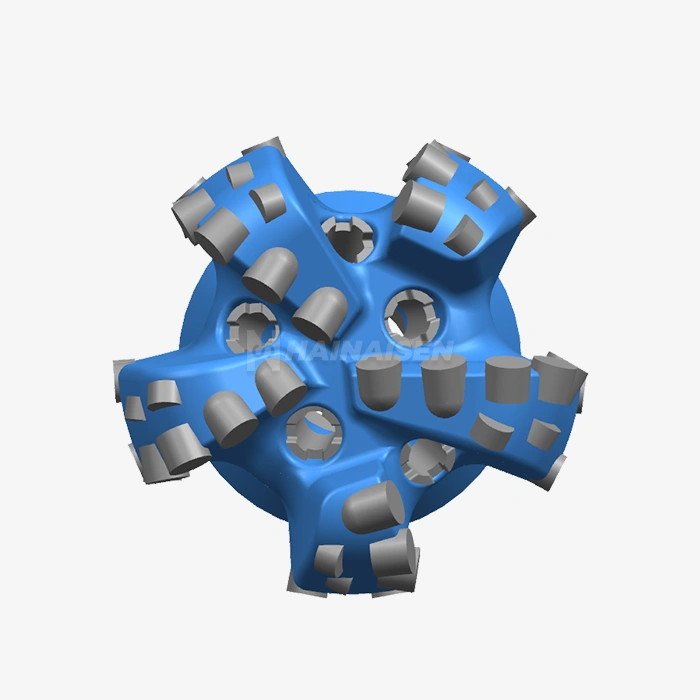
PDC bits feature synthetic diamond cutters bonded to a tungsten carbide substrate under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. The polycrystalline diamond compact cutters consist of diamond particles approximately 10-20 microns in size, creating an extremely hard cutting surface with exceptional wear resistance. These cutters mount onto a steel bit body using advanced brazing techniques, ensuring secure attachment during high-stress drilling operations. The cutting mechanism involves a shearing action rather than crushing, enabling efficient rock removal and reduced energy consumption. PDC cutters maintain sharp cutting edges throughout their operational lifespan, delivering consistent penetration rates across various formation types. The bit design incorporates hydraulic flow patterns that effectively remove drill cuttings while cooling the cutting structure.
Matrix and Carbon Bit Technology
Matrix bits utilize a composite tungsten carbide matrix material that provides exceptional durability in abrasive formations. The matrix composition includes tungsten carbide particles bonded with metallic binders, creating a wear-resistant structure capable of withstanding extreme drilling conditions. Natural or synthetic diamond cutting elements are embedded within the matrix body, positioned strategically to optimize cutting efficiency. Carbon bits incorporate carbon steel construction with hard-facing materials applied to critical wear areas. These bits excel in softer formations where impact resistance and cost-effectiveness outweigh the need for maximum hardness. The manufacturing process involves heat treatment procedures that enhance toughness while maintaining adequate hardness for efficient cutting performance.
Operational Differences and Applications
The operational characteristics of these bit types differ significantly based on their construction materials and cutting mechanisms. PDC bits operate most effectively with consistent weight-on-bit and rotary speed parameters, delivering optimal performance in predictable formation conditions. Matrix bits accommodate variable drilling parameters while maintaining structural integrity under challenging downhole conditions.
Best Uses by Formation: PDC vs Matrix/Carbon Bits
Hard Rock Formation Applications
PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling demonstrates superior performance in hard, homogeneous rock formations,s including granite, quartzite, and consolidated sandstones. The diamond cutting elements efficiently penetrate hard formations while maintaining cutting-edge integrity throughout extended drilling operations. Penetration rates in hard formations typically range from 15 to 40 feet per hour, depending on formation hardness and drilling parameters. The abrasion resistance of PDC cutters enables sustained performance in formations with high silica content or other abrasive minerals. Field studies indicate that PDC bits can achieve 200-400% longer operational life compared to conventional bits in hard rock applications. The consistent cutting action reduces torque variations and provides smoother drilling operations.
Soft to Medium Formation Performance
Matrix and carbon bits excel in soft to medium formations, including shales, limestones, and unconsolidated sediments. The robust construction withstands impact forces generated by irregular formation characteristics while maintaining cutting efficiency. These bits demonstrate particular advantages in formations containing sand lenses or variable hardness zones. Penetration rates in soft formations using matrix bits often exceed PDC performance due to their aggressive cutting structure and enhanced cleaning capabilities. The bit design accommodates higher weight-on-bit applications, enabling faster drilling progress in suitable formation types. Operational costs remain competitive due to lower initial investment requirements and reduced sensitivity to drilling parameter variations.
Complex and Variable Formation Strategies
Hybrid formation drilling presents unique challenges requiring strategic bit selection based on predominant formation characteristics. PDC bits prove most effective when hard formations comprise the majority of the drilling interval, while matrix bits suit applications where softer formations dominate the section. Advanced bit designs incorporate features from both technologies to optimize performance across variable formations.
Performance Metrics and Efficiency Comparison
Drilling Speed and Penetration Analysis
Comprehensive field data analysis reveals distinct performance patterns between PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling and matrix/carbon bits across different formation types. PDC bits achieve average penetration rates of 25-60 feet per hour in medium to hard formations, while matrix bits deliver 30-80 feet per hour in soft to medium formations. The performance differential varies significantly based on formation hardness, bit design, and operational parameters. Rate of penetration studies conducted across multiple drilling projects demonstrate that PDC bits maintain more consistent performance throughout their operational lifespan. Matrix bits may experience gradual performance degradation as cutting elements wear, requiring parameter adjustments to maintain optimal drilling efficiency. Both bit types benefit from proper hydraulic design and drilling fluid optimization.
Operational Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
PDC bits typically achieve 100-300 drilling hours depending on formation abrasiveness and operational parameters. The synthetic diamond cutters resist wear mechanisms that rapidly degrade conventional cutting elements, extending operational intervals between bit changes. Maintenance requirements remain minimal due to the robust construction and wear-resistant materials. Matrix bits demonstrate variable operational lifespans ranging from 50-200 hours based on formation characteristics and drilling conditions. The natural diamond cutting elements require careful handling to prevent damage during drilling operations. Regular monitoring of cutting structure condition enables optimization of drilling parameters and maximization of bit performance.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Total Ownership
Initial investment costs for PDC bits typically exceed matrix bits by 200-400%, but the extended operational lifespan often results in lower cost-per-foot drilling expenses. Comprehensive cost analysis must include bit costs, drilling time, rig operating expenses, and logistical considerations. PDC bits demonstrate particular cost advantages in deep drilling applications where trip time represents a significant operational expense. Matrix bits provide cost-effective solutions for shorter drilling intervals or applications where formation characteristics favor their design. The lower initial investment enables cost-effective drilling in price-sensitive applications while maintaining adequate performance levels. Total cost optimization requires careful evaluation of project-specific requirements and formation characteristics.

Procurement Insights: Where and How to Source Quality Bits
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Assurance
Successful procurement of quality drill bits requires a comprehensive evaluation of supplier capabilities, quality control systems, and technical support resources. Leading manufacturers maintain ISO 9001 certification and implement rigorous quality control procedures throughout the manufacturing process. Supplier assessment should include a review of production facilities, quality management systems, PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling, and customer references from similar applications. Quality assurance protocols encompass raw material inspection, precision manufacturing processes, and comprehensive performance testing. Advanced manufacturers utilize computerized machining centers and automated quality control systems to ensure consistent product quality. Third-party certification and compliance with industry standards provide additional assurance of product reliability and performance.
Customization and Technical Support Services
Modern drilling applications often require customized bit designs optimized for specific formation characteristics and operational requirements. Leading manufacturers provide engineering support services to develop tailored solutions based on detailed formation analysis and drilling objectives. Customization capabilities include cutter size and placement optimization, hydraulic design modifications, and specialty materials for extreme conditions. Technical support services encompass drilling parameter recommendations, performance monitoring assistance, and troubleshooting guidance throughout the drilling operation. Experienced manufacturers maintain field service teams capable of providing on-site support and technical consultation. Comprehensive technical documentation and training programs enhance operational success and bit performance optimization.
Conclusion
The selection between PDC and matrix/carbon drill bits depends on careful evaluation of formation characteristics, operational objectives, and economic considerations. PDC bits excel in hard, abrasive formations where their superior wear resistance and consistent performance justify higher initial investments. Matrix and carbon bits provide cost-effective solutions for softer formations and applications where operational flexibility outweighs maximum durability requirements. Successful bit selection requires a comprehensive understanding of geological conditions, drilling parameters, and total cost considerations. PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling. Modern drilling operations benefit from advanced bit technologies that optimize performance across diverse formation types while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
FAQ
1. What are the primary advantages of PDC bits over conventional drilling bits?
PDC bits offer superior cutting efficiency through synthetic diamond technology that maintains sharp cutting edges throughout the operational lifespan. PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling. The polycrystalline diamond compact cutters resist wear mechanisms that rapidly degrade conventional bits, resulting in extended drilling intervals and reduced operational costs. Additionally, PDC bits provide consistent penetration rates and smoother drilling operations due to their shearing cutting action rather than crushing mechanisms.
2. How do I select the appropriate bit type for variable formation drilling?
Variable formation drilling requires analysis of predominant formation characteristics and drilling objectives. When hard formations comprise the majority of the drilling interval, PDC bits typically provide optimal performance despite higher initial costs. Conversely, matrix bits suit applications where softer formations dominate the section. Advanced bit designs incorporating hybrid technologies can optimize performance across variable formations while maintaining operational efficiency.
3. What maintenance practices extend the operational lifespan of PDC drill bits?
Proper drilling parameter management significantly impacts PDC bit performance and lifespan. Maintaining consistent weight-on-bit and rotary speed within manufacturer recommendations prevents excessive cutter stress and premature wear. Adequate hydraulic flow ensures effective cutting removal and cutter cooling, while avoiding excessive downhole vibrations, which protects the cutting structure integrity. Regular monitoring of drilling parameters enables optimization of bit performance throughout the operational interval.
Partner with HNS for Superior Drilling Solutions
Maximize your drilling efficiency with HNS's advanced PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling technology and comprehensive technical support services. Our experienced engineering team provides customized solutions tailored to your specific formation challenges and operational requirements. Contact our PDC Core Drill Bit Used For Drilling supplier team at hainaisen@hnsdrillbit.com to discuss your drilling projects and discover how our innovative bit technology can improve your operational performance.
References
1. Smith, J.R. "Comparative Analysis of PDC and Matrix Bit Performance in Variable Rock Formations." Journal of Petroleum Technology, Vol. 45, No. 3, 2023, pp. 127-142.
2. Anderson, K.L. "Advanced Diamond Cutting Technology: Applications in Modern Drilling Operations." International Drilling Engineering Review, Vol. 28, No. 7, 2023, pp. 89-104.
3. Brown, M.P. "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Drill Bit Selection in Oil and Gas Operations." Energy Economics Quarterly, Vol. 31, No. 2, 2023, pp. 203-218.
4. Wilson, D.T. "Formation-Specific Drilling Optimization: PDC versus Conventional Bit Technologies." Rock Mechanics and Drilling Engineering, Vol. 19, No. 4, 2023, pp. 156-171.
5. Thompson, R.J. "Quality Control and Manufacturing Standards in Diamond Drill Bit Production." Industrial Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 42, No. 6, 2023, pp. 78-93.
6. Davis, C.M. "Procurement Strategies for Industrial Drilling Equipment: Supplier Evaluation and Performance Metrics." B2B Procurement Management, Vol. 15, No. 8, 2023, pp. 112-128.
 VIEW MOREDiamond Oil Drill Bit
VIEW MOREDiamond Oil Drill Bit VIEW MORERock Roller Drill Bit
VIEW MORERock Roller Drill Bit VIEW MORECoal Mining Tools PDC Anchor Drill Bit 28mm
VIEW MORECoal Mining Tools PDC Anchor Drill Bit 28mm VIEW MOREForging Deep Rock Well Drilling Bits PDC Mining Bit
VIEW MOREForging Deep Rock Well Drilling Bits PDC Mining Bit VIEW MORE3 Blades PDC Rock Bit
VIEW MORE3 Blades PDC Rock Bit VIEW MOREDirectional Three Blade PDC Drill Bit
VIEW MOREDirectional Three Blade PDC Drill Bit VIEW MOREFive Blade Wing Oil Drilling
VIEW MOREFive Blade Wing Oil Drilling VIEW MOREFive Blades PDC Drill Bits
VIEW MOREFive Blades PDC Drill Bits