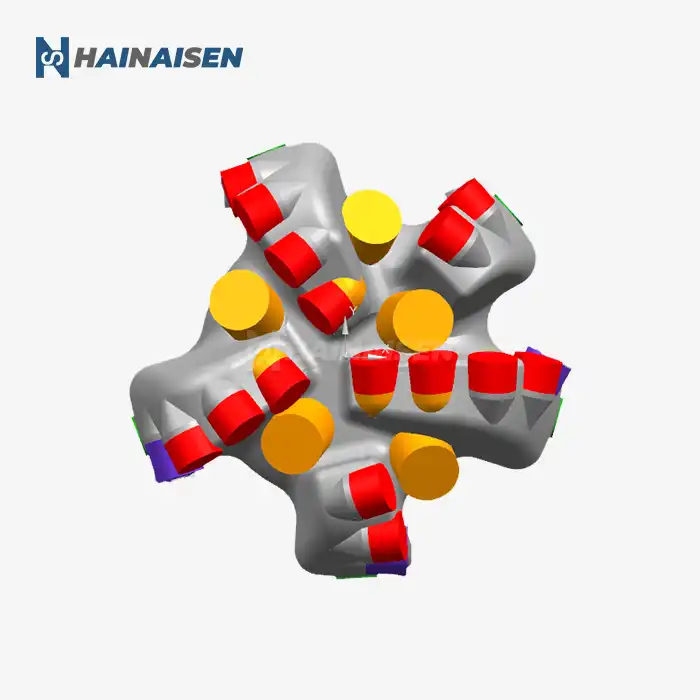
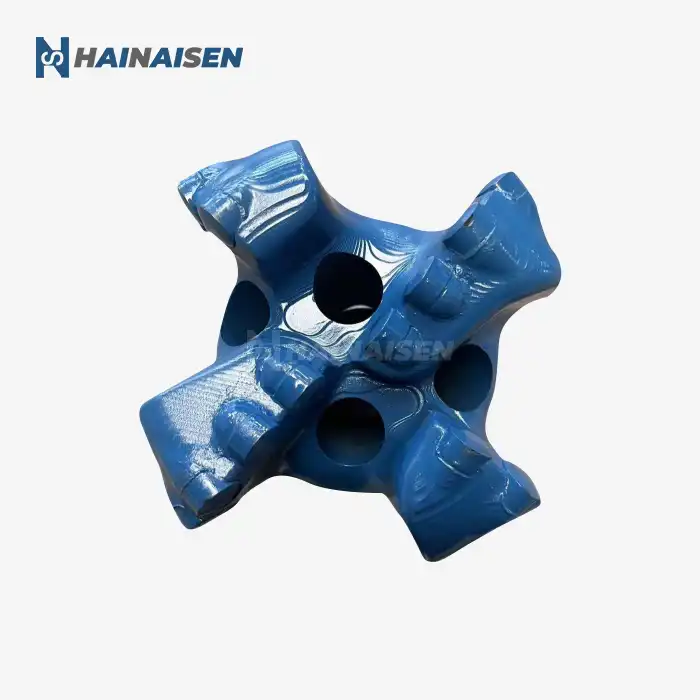
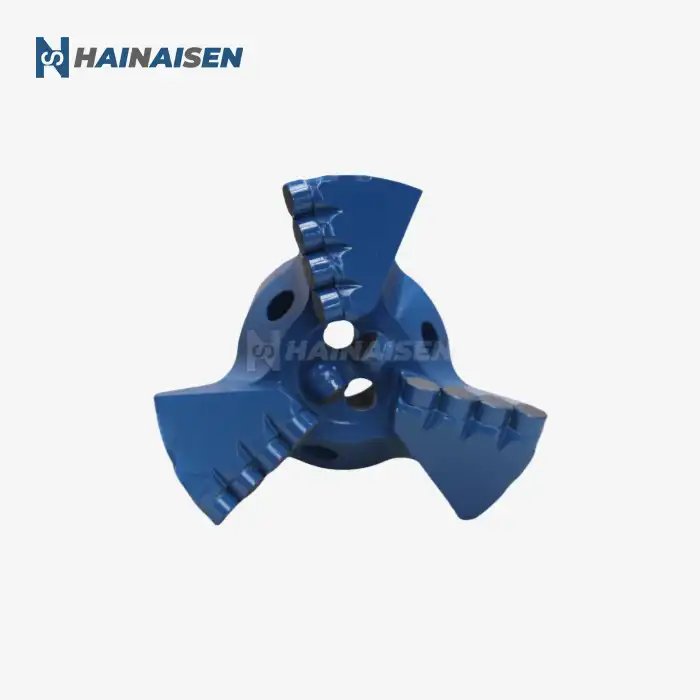
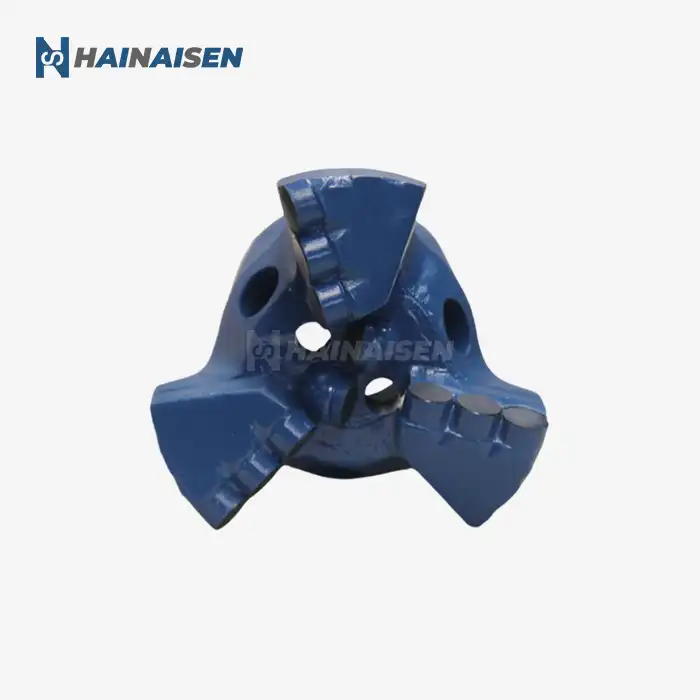
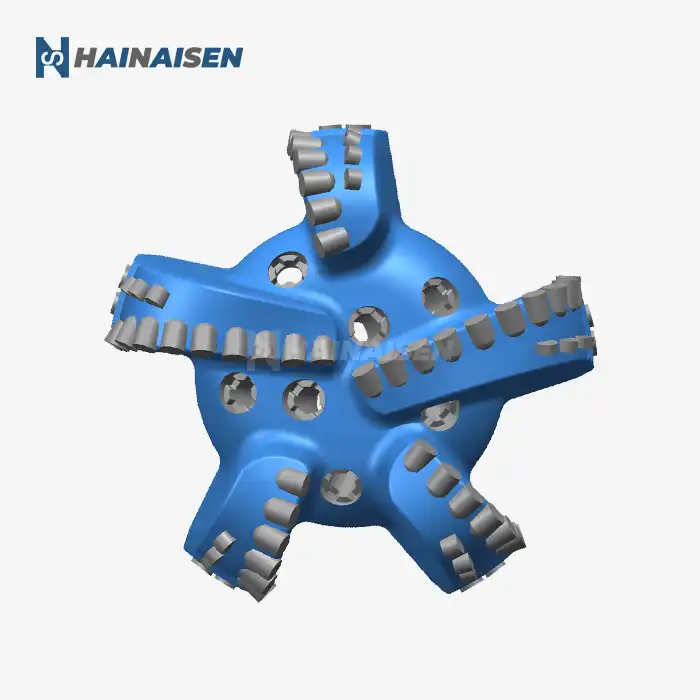
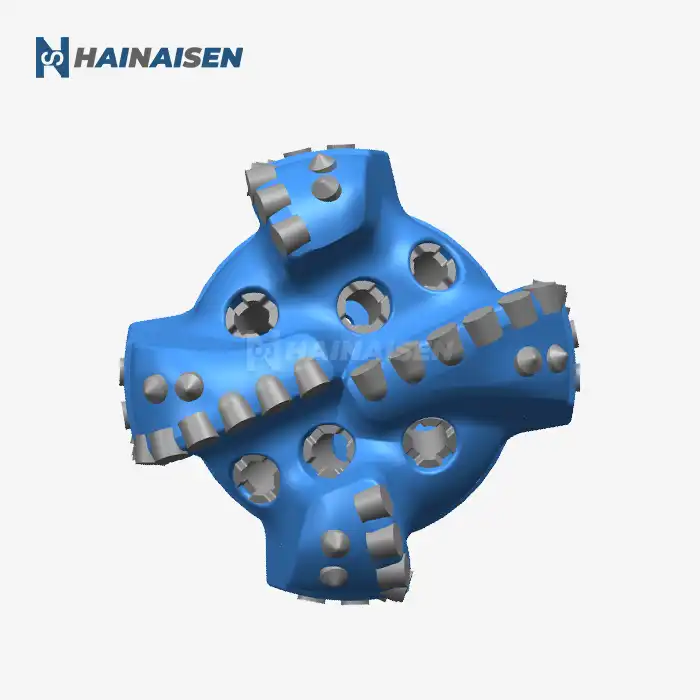
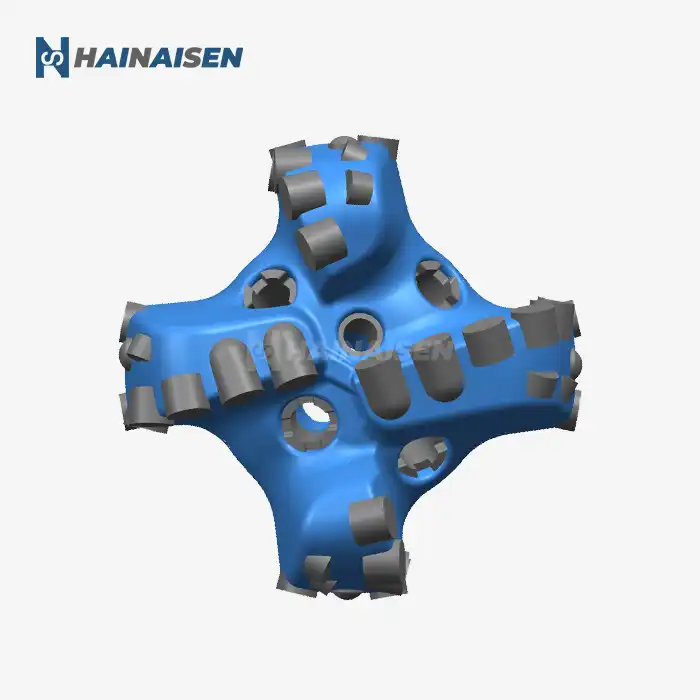
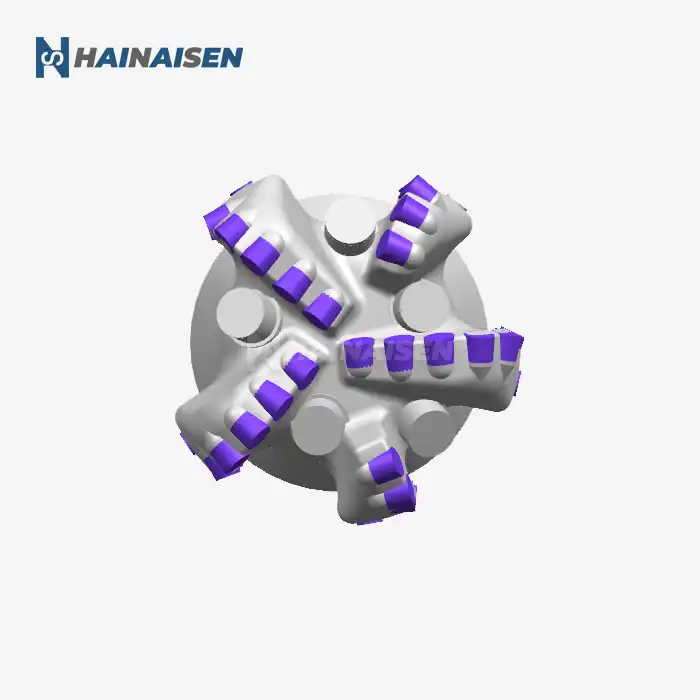
What makes 4-wing PDC bits effective in mining/water wells?
The effectiveness of 4-wing PDC bits in mining and water well applications stems from several key factors:
Enhanced Cutting Efficiency
These PDC bits' four-wing design greatly increases cutting efficiency. The bit produces a more aggressive and balanced cutting action by dividing the cutting force among four blades rather than the customary three. Increased penetration rates are possible with this design, particularly in medium-hardness rocks that are frequently found in water well and mining projects.
Improved Stability and Reduced Vibration
The increased stability of the 4 Wings Blades PDC Bit when in use is one of its best qualities. Because of the symmetrical four-wing arrangement, the forces are distributed more evenly, which lessens vibration and facilitates smoother drilling. For both mining and water well applications, this stability is very helpful in preserving wellbore quality and lowering the chance of deviation.
Optimized Hydraulics
The efficiency of 4-wing PDC bits is greatly influenced by their hydraulic design. In addition to minimizing bit balling and guaranteeing effective cooling of the cutting parts, the blade configuration improves fluid flow and cuttings removal. Maintaining constant drilling speeds and extending bit life, particularly in difficult formations, depend on this optimized hydraulic performance.
Versatility Across Formations
4-wing PDC bits demonstrate remarkable versatility across various geological strata. Their design allows them to perform effectively in a range of formations, from soft to medium-hard rocks. This adaptability makes them particularly suitable for mining operations where multiple rock types may be encountered, as well as for water well drilling through diverse subsurface layers.
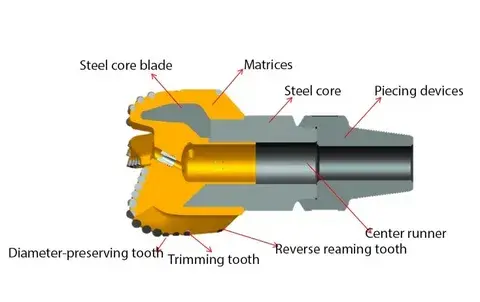
Design traits of 4-wing PDC bits for dual use
The design of 4-wing PDC bits incorporates several traits that make them suitable for both mining and water well applications:
Customizable Cutting Structure
One of the key design traits of 4 Wings Blades PDC Bit is the ability to customize the cutting structure. Manufacturers can adjust the number, size, and placement of PDC cutters on each blade to optimize performance for specific formation types. This flexibility allows for the creation of bits that can efficiently drill through the varied lithologies encountered in both mining and water well projects.
Balanced Aggressiveness
The design of 4-wing PDC bits strikes a balance between aggressiveness and stability. The four-wing configuration allows for a more aggressive cutting action compared to three-blade designs, while still maintaining the stability required for straight-hole drilling. This balanced approach is particularly beneficial in water well applications where maintaining verticality is crucial, as well as in mining operations where both penetration rate and hole quality are important.
Junk Slot Area Optimization
The design of 4-wing PDC bits includes optimized junk slot areas between the blades. These spaces facilitate the efficient removal of cuttings and prevent bit balling, which is essential for maintaining drilling performance in both mining and water well applications. The increased junk slot area also contributes to improved hydraulic efficiency, allowing for better cleaning and cooling of the bit face.
Durability-Focused Features
Recognizing the demanding nature of both mining and water well drilling, 4-wing PDC bits incorporate durability-focused design traits. These may include reinforced blade structures, impact-resistant cutter placement, and wear-resistant materials on critical surfaces. Such features ensure the bit can withstand the rigors of drilling through varied formations, from abrasive sandstones to sticky shales.
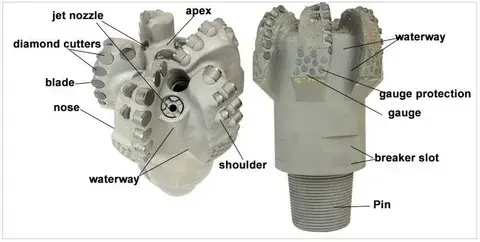
Structural and material advantages in 4-wing PDC bits
The structural and material composition of 4-wing PDC bits contributes significantly to their performance and longevity:
Advanced Steel Body Construction
The core structure of 4 Wings Blades PDC Bit typically consists of a high-quality steel body. This construction provides the necessary strength and rigidity to withstand the high torque and weight-on-bit encountered during drilling operations. The steel body also offers excellent heat dissipation properties, crucial for maintaining the integrity of the bit during extended drilling runs.
Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) Cutters
Advanced polycrystalline diamond compact material is used to make the cutting parts of 4-wing PDC bits. When it comes to wear resistance, these PDC cutters are better than standard tungsten carbide inserts. Its high toughness and resistance to wear make the diamond layer very useful. This lets the bit keep cutting well for longer, even in tough formations.
Specialized Matrix Materials
Specialized matrix materials are used to make a lot of 4-wing PDC bits. These substances, which are usually made of tungsten carbide, are used to make the bit more resistant to wear and temperature changes. The matrix helps protect the steel body from wear and tear and gives extra support to the PDC cuts, which makes the bit last longer.
Optimized Blade Geometry
In 4-wing PDC bits, the blades' structure is carefully designed to strike a balance between cutting efficiency and durability. This machine's blade profile, which includes blade height, width, and spiral angle, is designed to remove as much rock as possible while keeping directional control and sound to a minimum. When working in mining and water well drilling, where conditions can change quickly, this optimized geometry is especially helpful for keeping performance steady.
Reinforced Gauge Protection
A lot of 4-wing PDC bits have extra gauge protection to keep the hole's width and stop undergauge holes. That's possible because the gauge pads are made of materials that don't wear down easily, and the PDC cuts are placed strategically on the bit's shoulder. The better gauge protection is very important for keeping the digging going quickly and making sure the quality of the finished borehole in both water well and mining situations.
Conclusion
Drilling technology for water well and mining applications has advanced significantly with the 4 Wings Blades PDC Bit. For operators looking to increase performance and efficiency in their drilling operations, its distinctive design features, along with structural and material advantages, make it a great option.
Are you looking to optimize your mining or water well drilling operations? Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in developing cutting-edge drilling solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our team of experienced engineers can work with you to design and manufacture custom 4 Wings Blades PDC Bits that maximize performance in your target formations. Whether you're a large oil service company requiring high-quality, long-lasting bits, or a water well drilling team seeking cost-effective solutions, we have the expertise and capabilities to meet your requirements. Take advantage of our state-of-the-art 3,500m² facility equipped with advanced processing equipment and a dedicated R&D team. Contact us today at hainaisen@hnsdrillbit.com to discover how our innovative 4 Wings Blades PDC Bits can revolutionize your drilling projects.
References
1. Smith, J.R. (2022). Advancements in PDC Bit Technology for Mining Applications. Journal of Mining Engineering, 45(3), 123-135.
2. Johnson, A.B., & Williams, C.D. (2021). Comparative Analysis of 3-Wing vs 4-Wing PDC Bits in Water Well Drilling. Groundwater, 59(2), 267-280.
3. Chen, X., et al. (2023). Structural Optimization of PDC Bits for Improved Performance in Medium-Hardness Formations. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 152, 105083.
4. Thompson, R.L. (2020). Materials Science in Modern Drill Bit Design: A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 32, 345-358.
5. Garcia, M.E., & Lopez, K.T. (2022). Hydraulic Efficiency of Multi-Wing PDC Bits in Various Geological Settings. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 74(8), 62-75.
6. Wilson, D.A. (2021). Economic Impact of Advanced PDC Bit Designs in Mining and Water Well Industries. Resources Policy, 70, 101965.