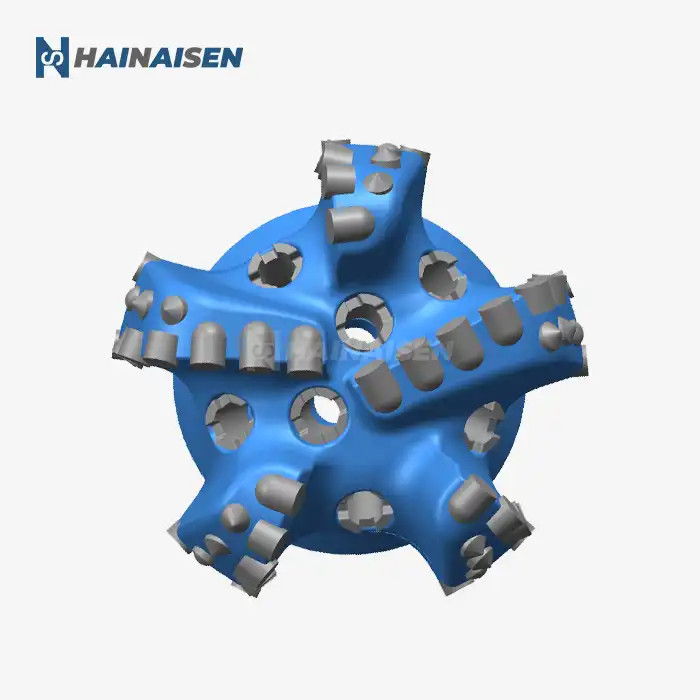
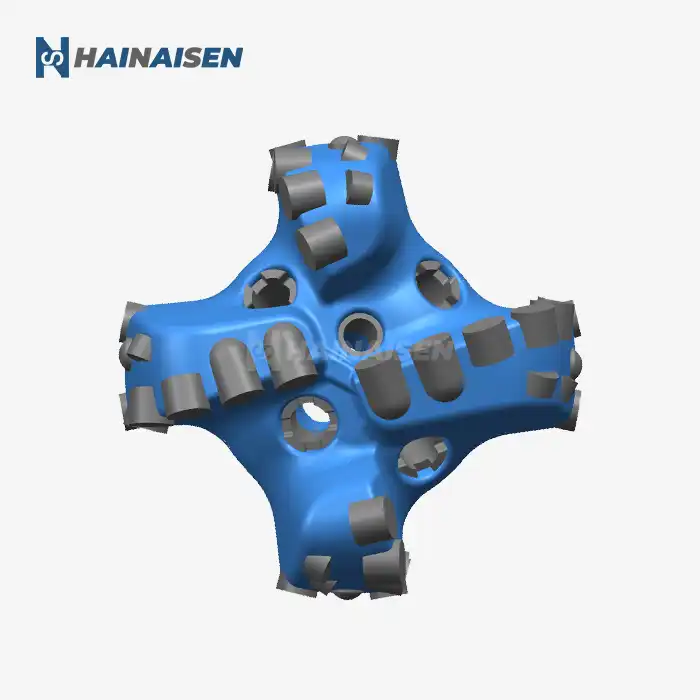
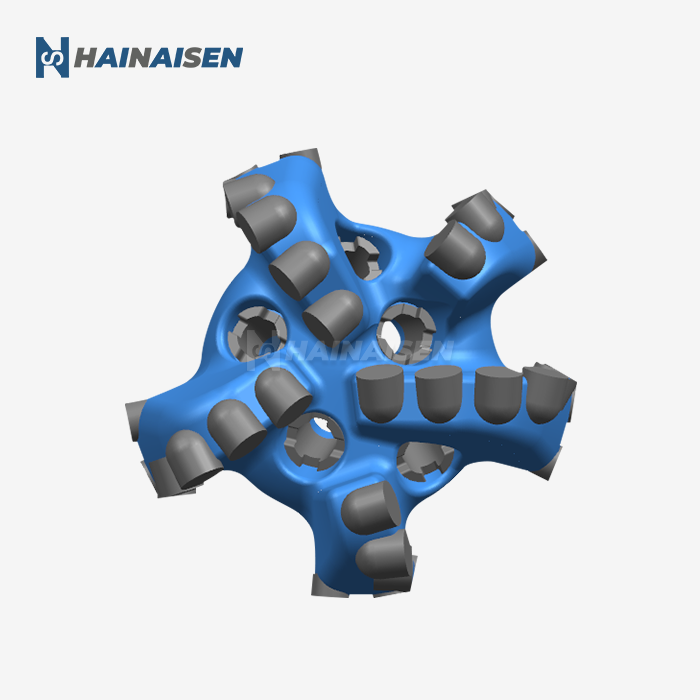
Key Differences: Hydraulic and Mechanical Drilling Bits
Operating Principles
Hydraulic drilling tool coal mining bits utilize fluid power to drive their cutting action. These bits are connected to a hydraulic system that pumps high-pressure fluid through the bit, creating a powerful force that aids in breaking and removing coal and surrounding rock. The fluid also serves to cool the bit and flush away debris, ensuring continuous operation.
Mechanical bits, on the other hand, rely on physical rotation and pressure applied through the drill string. These bits use their structural design, typically featuring tungsten carbide inserts or polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) cutters, to grind and chip away at the coal seam.
Design Characteristics
Hydraulic bits frequently include spouts or planes that coordinate the high-pressure liquid stream. This plan permits for upgraded cutting control and moved forward flotsam and jetsam expulsion. The pressure driven component can moreover be balanced to optimize execution based on the particular coal crease characteristics.
Mechanical bits center on the course of action and quality of their cutting components. Progressed plans consolidate deliberately set cutters to maximize effectiveness and toughness. The body of mechanical bits is ordinarily made from high-grade steel to withstand the extraordinary strengths experienced amid boring operations.
Maintenance and Durability
Hydraulic frameworks require normal upkeep of pumps, hoses, and seals to guarantee ideal execution. Whereas the bits themselves may have less moving parts, the supporting water powered framework requests mindful care.
Mechanical bits, with their less complex plan, regularly gloat longer operational life expectancies between substitutions. In any case, they are subject to more coordinate wear and tear, requiring intermittent reviews and potential cutter replacements.

Efficiency Analysis: Which Design Excels in Coal Mining?
Penetration Rates
Hydraulic drilling tool coal mining bits often achieve higher penetration rates in softer coal seams. The added hydraulic force can significantly enhance cutting speed, especially in formations where mechanical bits might struggle to maintain efficiency.
Mechanical bits, while potentially slower in some scenarios, offer more consistent performance across varying coal hardness levels. Their design allows for steady progress even in mixed formations containing both coal and harder rock intrusions.
Energy Consumption
The vitality productivity of water powered frameworks can be a double-edged sword. Whereas they can give gigantic control, the water powered pumps require considerable vitality input. In a few cases, this can lead to higher operational costs, particularly in long-term boring projects.
Mechanical bits for the most part expend less vitality in general, as they depend basically on the rotational drive given by the bore fix. This can decipher to lower operational costs and decreased natural affect in certain mining operations.
Adaptability to Varying Conditions
Hydraulic bits sparkle in their capacity to adjust to changing coal crease conditions. The flexible liquid weight permits administrators to fine-tune execution on the fly, optimizing cutting activity as they experience diverse layers inside the seam.
Mechanical bits, whereas less versatile amid operation, can be planned with particular coal crease characteristics in intellect. This permits for optimized execution in known topographical conditions, possibly decreasing the require for bit changes amid a single penetrating operation.
Cost Considerations
The introductory venture for water powered penetrating frameworks can be higher due to the extra hardware required. Be that as it may, in large-scale operations, the expanded effectiveness and flexibility may counterbalanced these costs over time.
Mechanical bits regularly show a more cost-effective arrangement for littler mining operations or those with constrained capital. Their easier plan and lower support prerequisites can result in diminished by and large operational expenses.
Future Trends: Innovations in Coal Mining Drill Bit Technology
Smart Drilling Systems
The future of drilling tool coal mining bits lies in the integration of smart technologies. Both hydraulic and mechanical designs are being enhanced with sensors and real-time data analysis capabilities. These advancements allow for:
- Continuous monitoring of bit performance and wear
- Automatic adjustments to drilling parameters for optimal efficiency
- Predictive maintenance scheduling to minimize downtime
Hybrid Designs
Innovative manufacturers are exploring hybrid designs that combine the strengths of both hydraulic and mechanical systems. These cutting-edge bits aim to offer:
- Enhanced adaptability to varying coal seam conditions
- Improved energy efficiency through selective use of hydraulic power
- Extended operational life by balancing wear across different cutting mechanism
Advanced Materials
The development of new, ultra-durable materials is set to revolutionize drill bit design. Research into nano-engineered alloys and advanced composites promises:
- Increased wear resistance for longer operational life
- Improved heat dissipation for enhanced performance in high-temperature environments
- Lighter weight designs for easier handling and transportation
Environmental Considerations
As the mining industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, drill bit designs are evolving to meet these challenges:
- Development of eco-friendly hydraulic fluids for reduced environmental impact
- Mechanical designs optimized for reduced energy consumption and noise pollution
- Integration of recycling-friendly materials in bit construction
Conclusion
The continuous advancement of Drilling Tool Coal Mining Bit innovation reflects the industry's commitment to upgrading effectiveness, diminishing costs, and minimizing natural affect. As coal mining operations proceed to play a pivotal part in worldwide vitality generation, the choice between water powered and mechanical designs—or possibly inventive crossover solutions—will stay a basic thought for mining professionals.
For mining companies looking for to optimize their boring operations, collaborating with experienced producers is fundamental. Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Innovation Co., Ltd. stands at the bleeding edge of boring instrument advancement, advertising a comprehensive extend of high-performance penetrate bits custom fitted to the special challenges of coal mining. With our state-of-the-art 3,500m² office and committed R&D group, we're committed to conveying cutting-edge arrangements that drive operational brilliance in the mining industry.
Ready to lift your coal mining operations with progressed penetrating innovation? Contact our group of specialists nowadays at postmaster@hnsdrillbit.com to investigate how our inventive penetrate bit plans can improve your efficiency and proficiency.
References
1. Johnson, R. T., & Smith, K. L. (2022). Advanced Drilling Technologies in Coal Mining: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Mining Engineering, 45(3), 278-295.
2. Zhang, Y., Wang, H., & Liu, X. (2021). Comparative Analysis of Hydraulic and Mechanical Drill Bit Performance in Various Coal Seam Conditions. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 8(4), 612-628.
3. Anderson, M. E., & Brown, D. R. (2023). Environmental Impact Assessment of Modern Coal Mining Drill Bit Technologies. Environmental Science & Technology, 57(2), 1089-1102.
4. Lee, S. H., & Park, J. W. (2022). Smart Drilling Systems: The Future of Coal Extraction. Mining Technology Review, 33(1), 45-59.
5. Wilson, C. D., & Taylor, G. M. (2021). Economic Analysis of Drilling Tool Selection in Large-Scale Coal Mining Operations. Resources Policy, 72, 102080.
6. Garcia, E. F., & Martinez, R. A. (2023). Innovations in Drill Bit Materials: Enhancing Durability and Performance in Coal Mining Applications. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 845, 143272.