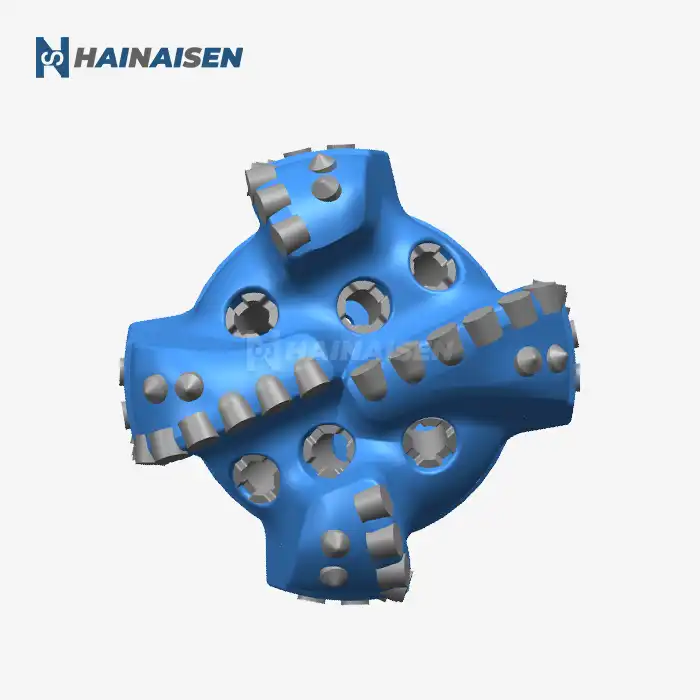
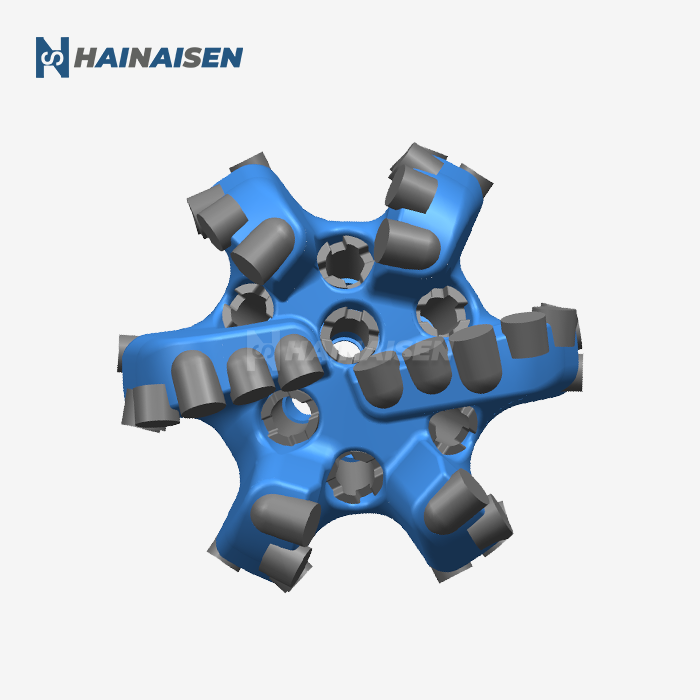
Optimizing Bit Design for Directional Drilling
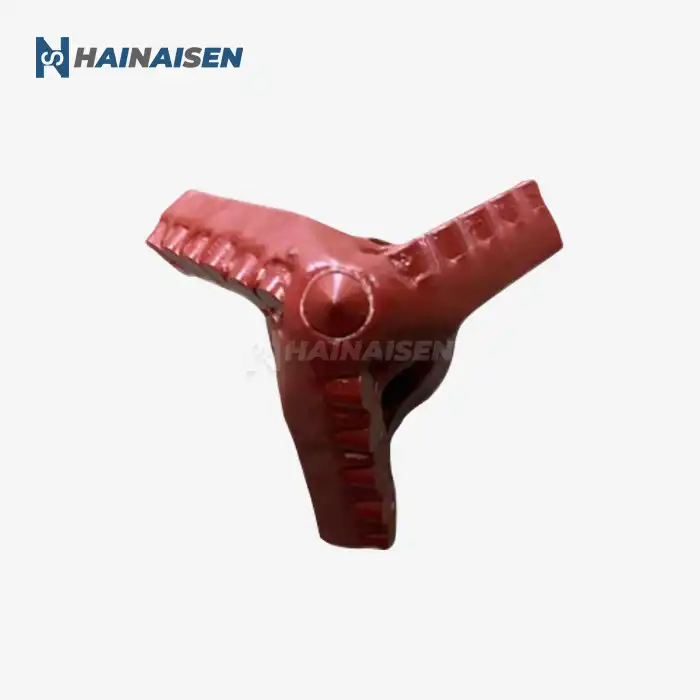
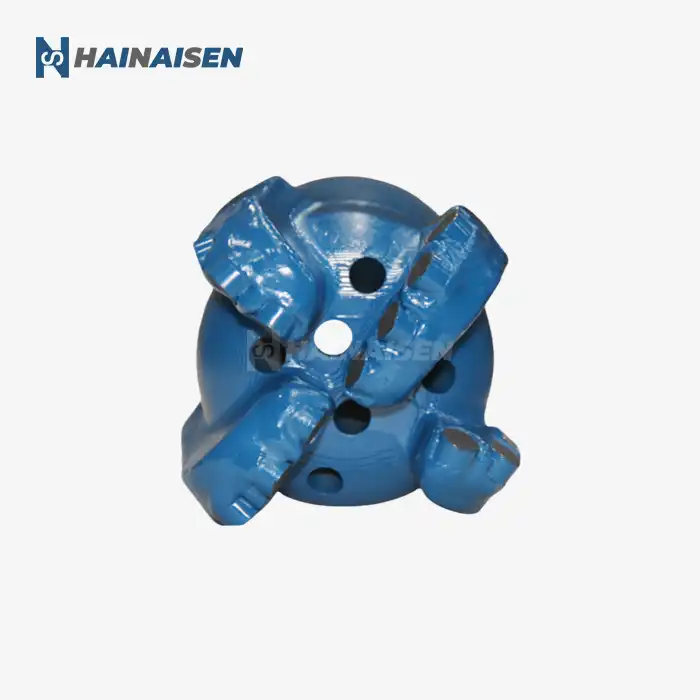
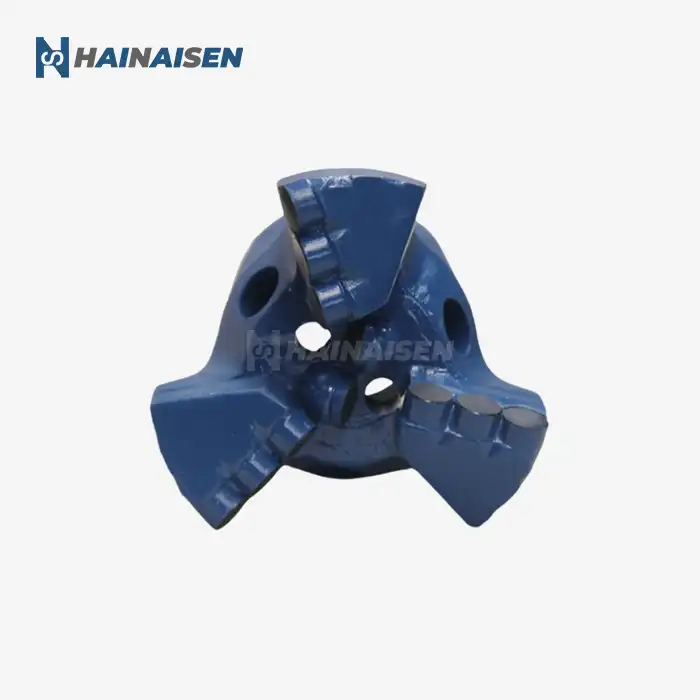
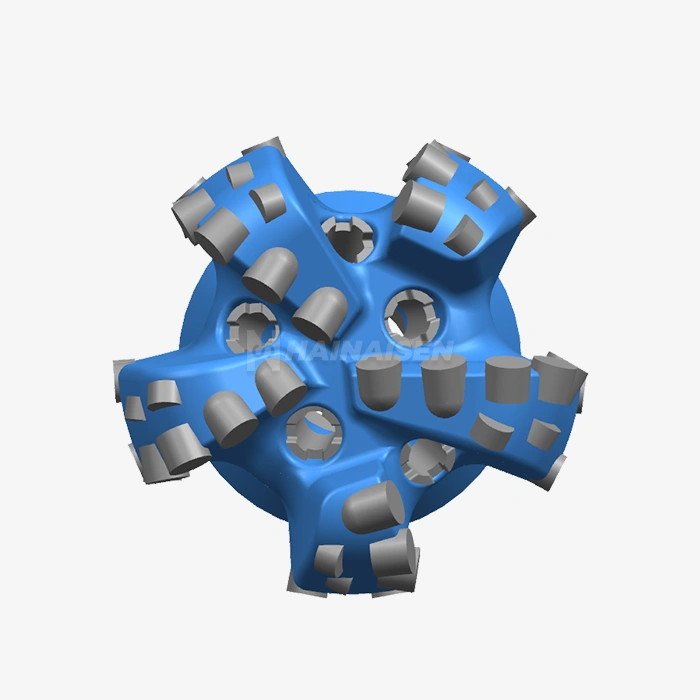
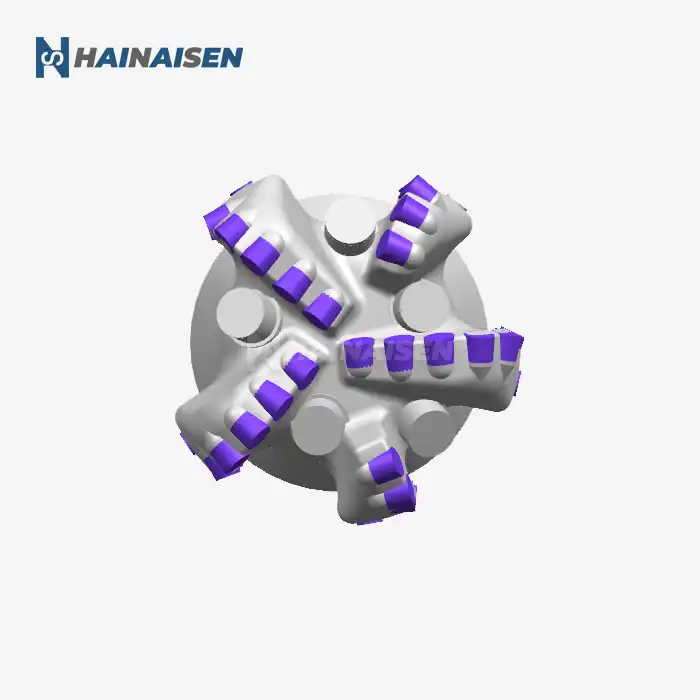
The foundation of reducing torque and drag in directional drilling starts with the design of the Directional Well PDC Drill Bit itself. Modern bit designs incorporate several features specifically tailored to enhance directional drilling performance:
Customized Cutter Placement and Geometry
Advanced PDC bits now feature strategically placed cutters with optimized geometries. These designs consider the specific formation characteristics and planned wellbore trajectory. By carefully positioning cutters and adjusting their back rake and side rake angles, manufacturers can create bits that cut more efficiently while reducing lateral forces that contribute to torque and drag.
Asymmetric Blade Configurations
Innovative asymmetric blade designs help balance cutting forces and improve directional response. These configurations can include varying blade lengths, spacing, and profiles that work together to minimize bit whirl and enhance stability. The result is a smoother drilling operation with reduced torque fluctuations and improved wellbore quality.
Enhanced Gauge Pad Design
The gauge area of a PDC bit plays a crucial role in directional control and borehole quality. Modern bits incorporate active gauge designs with strategically placed diamond elements or PDC inserts. These features help maintain gauge while reducing friction and providing additional cutting action, contributing to lower torque and drag in directional sections.
Hydraulic Optimization
Efficient cutting evacuation is essential for reducing torque and drag. Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling allows for the optimization of nozzle placement and hydraulic channels within the bit body. This ensures proper cleaning of the cutting structure and improved fluid flow around the bit, reducing the likelihood of bit balling and minimizing torque-inducing effects.
Lubrication Techniques for Reduced Friction
While bit design plays a significant role in torque and drag reduction, effective lubrication strategies can further enhance drilling performance in directional wells:
High-Performance Drilling Fluids
The selection of appropriate drilling fluids is crucial for minimizing friction between the drillstring and the wellbore. Advanced synthetic-based muds (SBMs) and high-performance water-based muds (HWBMs) can significantly reduce the coefficient of friction, especially in highly deviated and horizontal sections. These fluids often contain specialized lubricants and friction reducers that form a thin film on metal surfaces, decreasing torque and drag.
Lubricant Additives
Incorporating lubricant additives into the drilling fluid can provide additional friction reduction benefits. These additives may include: - Beads or microbeads that act as rolling elements between surfaces - Nanoparticles that enhance the lubricating properties of the base fluid - Graphene-based additives that create ultra-low friction coatings on metal surfaces
Wellbore Conditioning
Regular wellbore conditioning can help maintain a smooth borehole surface and reduce friction. This process involves circulating drilling fluid at high rates and rotating the drillstring to remove cuttings beds and smooth out any irregularities in the wellbore wall. Proper conditioning can significantly reduce torque and drag, especially in extended-reach wells.
Specialized Coatings
Applying low-friction coatings to drillpipe and bottomhole assembly (BHA) components can further reduce friction in directional wells. These coatings, such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) or specialized polymer coatings, can significantly decrease the coefficient of friction between the drillstring and the wellbore, leading to reduced torque and drag.
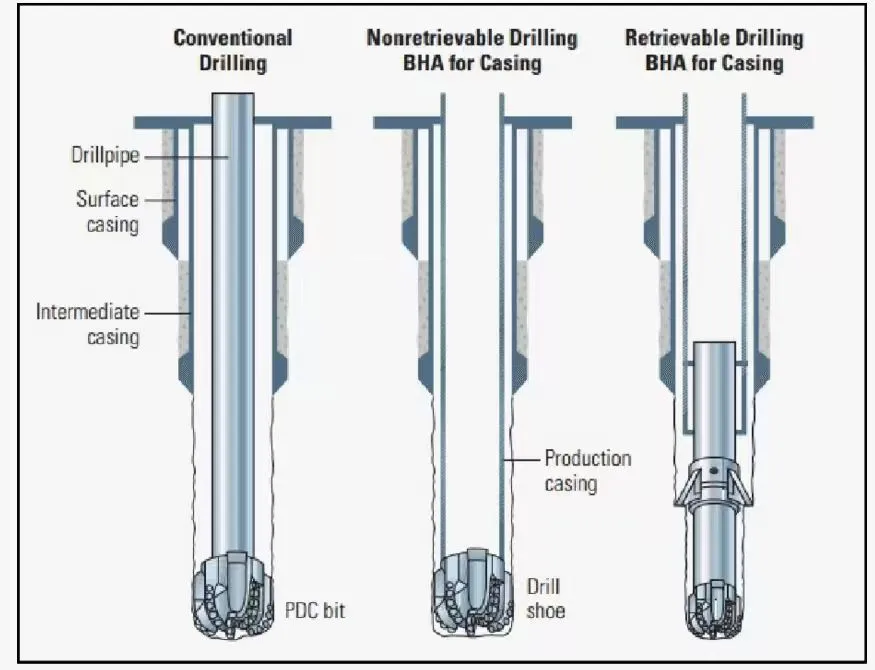
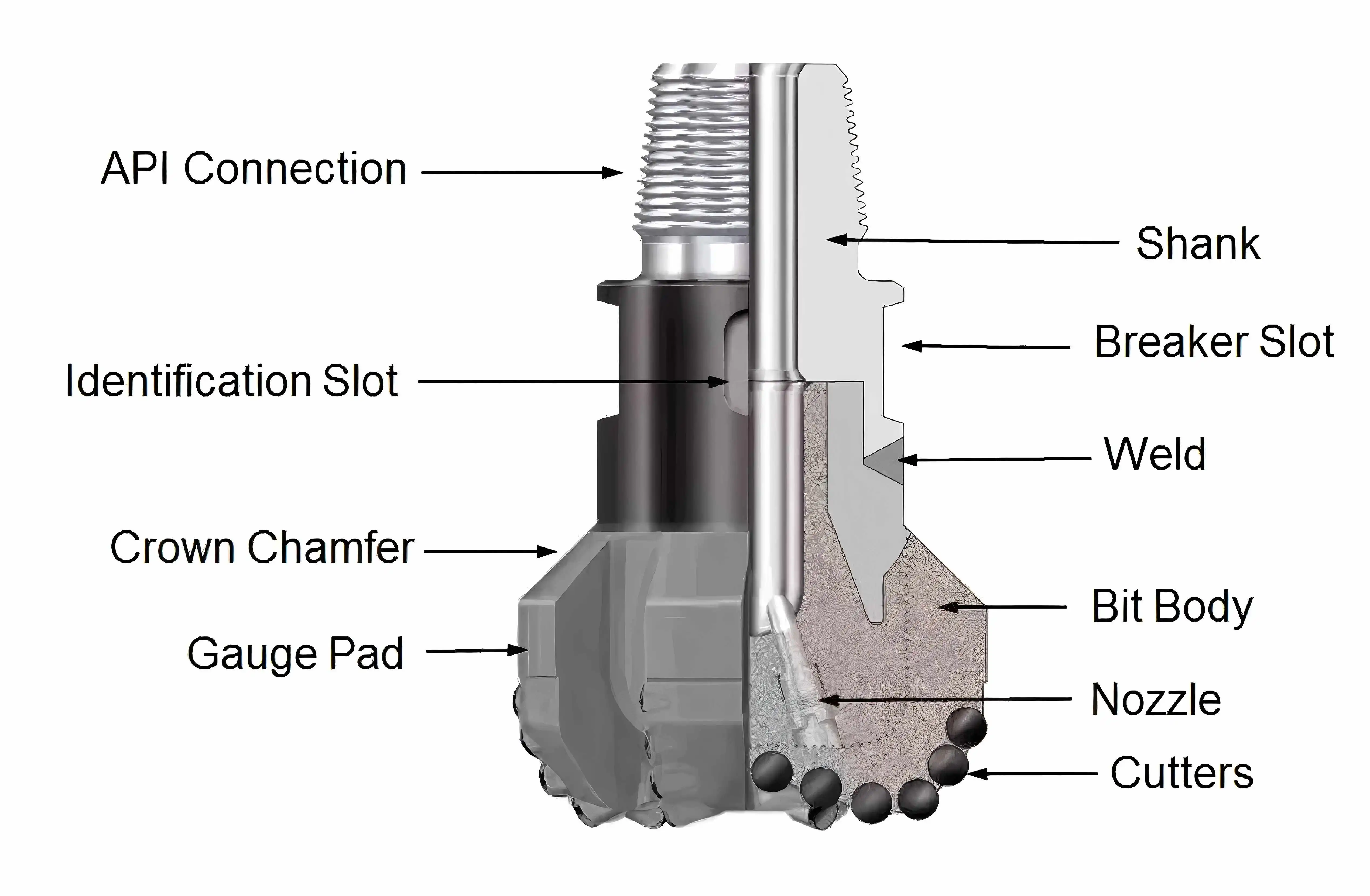
Directional Well PDC Drill Bit
Choosing a Directional Well PDC Drill Bit can also contribute to friction reduction in directional wells. The fixed cutter design of PDC bits provides superior stability and better directional control, which can be crucial for minimizing torque and drag, especially in deep or complex well profiles. When combined with the right lubrication techniques, a Directional Well PDC Drill Bit can significantly improve drilling efficiency, reduce wear, and extend bit life.
Torque Management in Horizontal Wells
Effective torque management is crucial for successful drilling operations, especially in horizontal and extended-reach wells where torque and drag issues are most pronounced:
Real-Time Monitoring and Modeling
Implementing advanced real-time monitoring systems allows operators to track torque and drag throughout the drilling process. These systems use sophisticated sensors and data analysis algorithms to provide instant feedback on downhole conditions. By combining this real-time data with predictive torque and drag models, drilling teams can make informed decisions to optimize drilling parameters and mitigate potential issues before they escalate.
Rotary Steerable Systems (RSS)
Rotary steerable systems have revolutionized directional drilling by allowing continuous rotation of the drillstring while steering. This continuous rotation helps distribute torque more evenly along the string, reducing the risk of stick-slip and other torsional vibrations. Advanced RSS tools also offer precise directional control, enabling smoother wellbore trajectories that inherently reduce torque and drag.
Optimized Weight on Bit (WOB) and Rotary Speed
Carefully managing weight on bit and rotary speed is essential for controlling torque in horizontal wells. Finding the right balance between these parameters can help maintain a steady rate of penetration while minimizing torsional vibrations and stick-slip. Directional Well PDC Drill Bits designed for specific formations and drilling conditions can help operators achieve this optimal balance more easily.
Drillstring Design and Configuration
The composition and configuration of the drillstring play a significant role in torque management. Utilizing tools such as: - Roller reamers to reduce friction in tight spots - Non-magnetic drill collars to improve weight distribution - Specialized tubulars with higher torsional strength in critical sections can all contribute to better torque management and reduced drag in horizontal wells.
Automated Drilling Systems
The implementation of automated drilling systems can significantly improve torque management in directional wells. These systems use advanced algorithms to continuously adjust drilling parameters based on real-time downhole conditions. By rapidly responding to changes in torque and drag, automated systems can maintain optimal drilling efficiency while minimizing the risk of stuck pipe or other torque-related issues.
In conclusion, reducing torque and drag in directional wells requires a multifaceted approach that combines advanced Directional Well PDC Drill Bit design, effective lubrication strategies, and sophisticated torque management techniques. By implementing these strategies, operators can achieve smoother drilling operations, improved wellbore quality, and enhanced overall drilling performance in challenging directional and horizontal well environments.
Are you looking to optimize your directional drilling operations and reduce torque and drag issues? Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in developing cutting-edge PDC drill bits and integrated technical solutions tailored to your specific drilling needs. Our advanced 3,500m² facility and dedicated R&D team ensure that we can deliver high-quality, custom-designed bits that excel in challenging directional drilling environments. Whether you're involved in oil and gas extraction, coal mining, or geological surveying, our expertise can help you achieve superior drilling performance and efficiency. Contact us today at hainaisen@hnsdrillbit.com to discover how our innovative Directional Well PDC Drill Bits can transform your drilling operations and drive your project success.
References
1. Smith, J.R. and Brown, T.L. (2022). Advanced PDC Bit Designs for Directional Drilling: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 74(5), 62-78.
2. Johnson, A.K., et al. (2021). Lubrication Strategies for Reducing Friction in Horizontal Wells. SPE Drilling & Completion, 36(3), 245-259.
3. Chen, X. and Wang, Y. (2023). Real-Time Torque and Drag Monitoring in Extended-Reach Wells: Case Studies and Best Practices. Offshore Technology Conference Proceedings, OTC-24680-MS.
4. Thompson, R.S. (2022). Optimizing Rotary Steerable System Performance in High-Angle and Horizontal Wells. SPE/IADC Drilling Conference Proceedings, SPE-208770-MS.
5. Lee, M.H., et al. (2023). Automated Drilling Systems: The Future of Torque Management in Directional Wells. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 220, 110320.
6. Wilson, G.P. and Davis, E.L. (2022). Innovative Drillstring Designs for Improved Torque Distribution in Horizontal Wells. International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Technology, 29(4), 389-405.