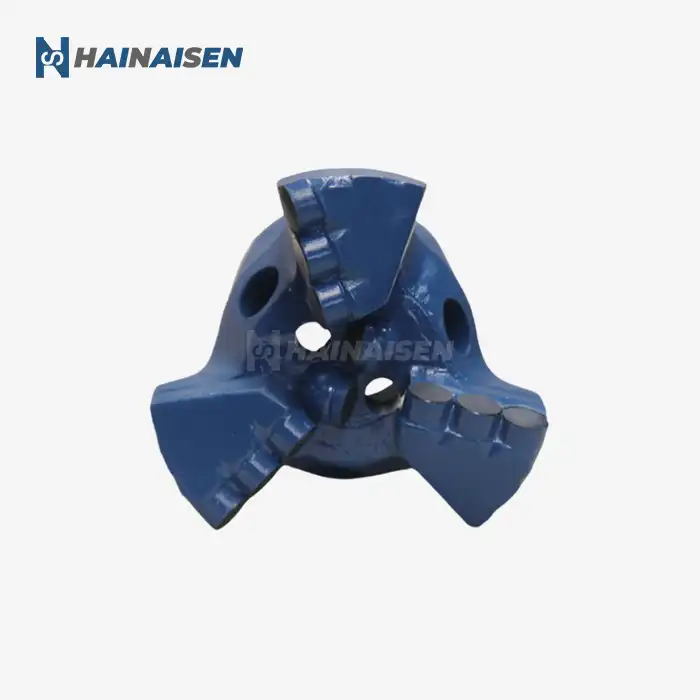
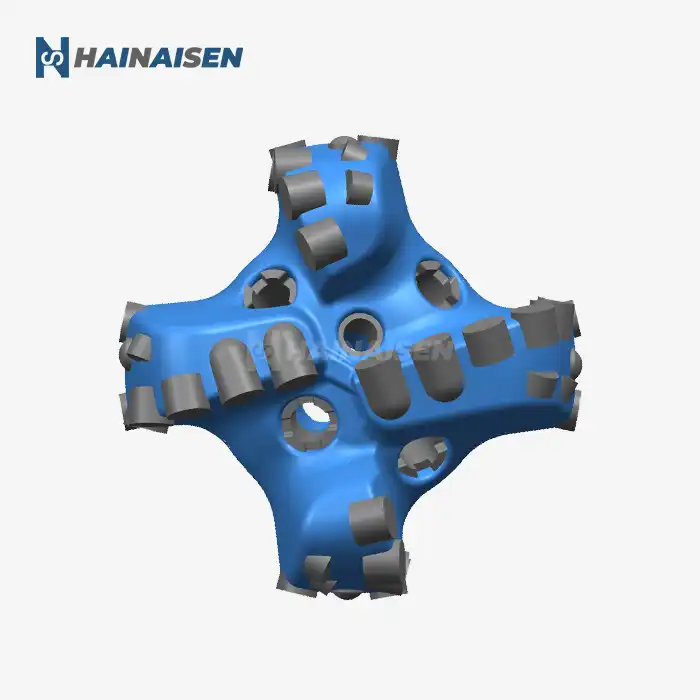
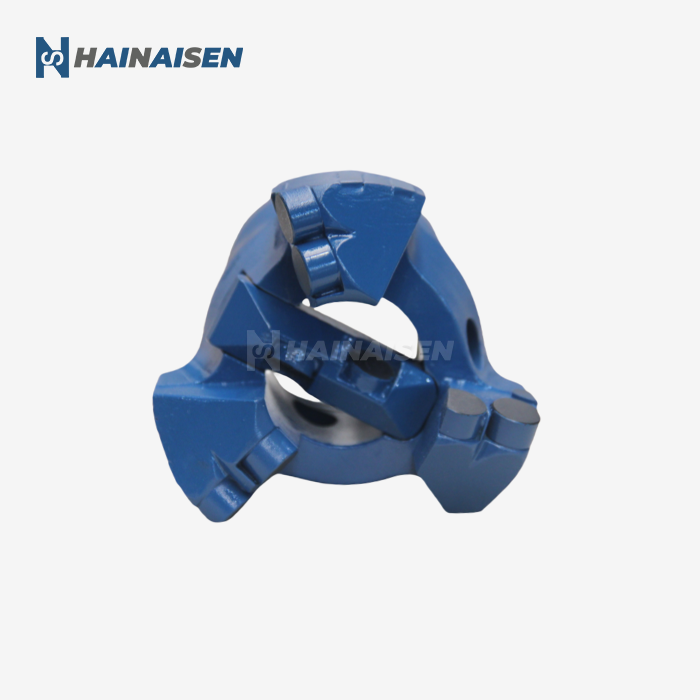
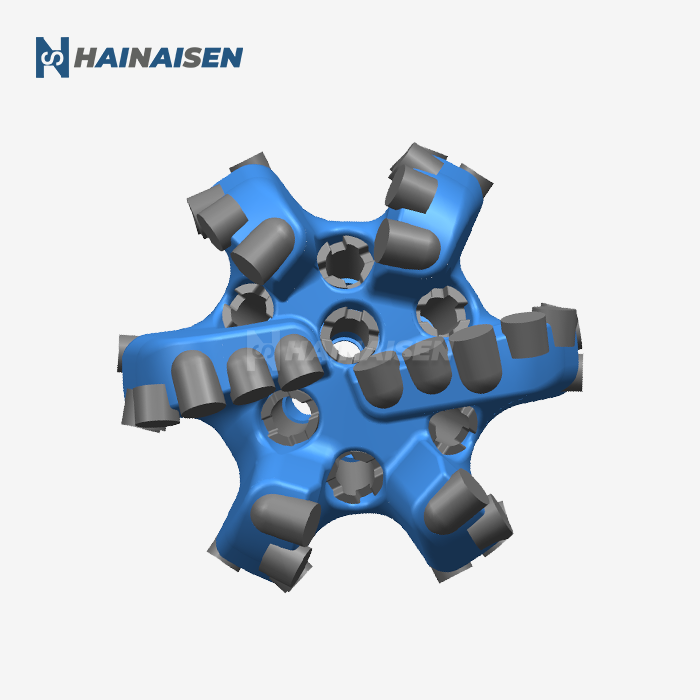
4 Blade vs. 6 Blade PDC Bit Dynamics in Directional Wells
When comparing the dynamics of 4-blade and 6-blade PDC bits in directional wells, several key factors come into play. The reduced blade count of a Four Blade PDC Drill Bit offers distinct advantages in certain directional drilling scenarios:
Maneuverability and Steering Response
Four-blade bits for the most part display way better maneuverability and directing reaction in directional wells. The decreased contact range with the wellbore permits for more exact control over the bit's heading, making it simpler to explore complex well directions. This improved responsiveness is especially useful when penetrating through arrangements with shifting hardness or when making visit directional changes.
Reduced Torque and Drag
The less edges on a four-blade bit result in lower torque prerequisites and decreased drag powers compared to six-blade plans. This characteristic is particularly invaluable in extended-reach directional wells, where minimizing torque and drag is pivotal for keeping up penetrating productivity and maintaining a strategic distance from stuck pipe incidents.
Formation Adaptability
Four-blade PDC bits demonstrate superior adaptability when transitioning between different formation types. The larger junk slots and more open cutting structure allow for better cleaning and prevent bit balling in softer formations, while still maintaining sufficient cutting elements for effective removal of harder rock layers.
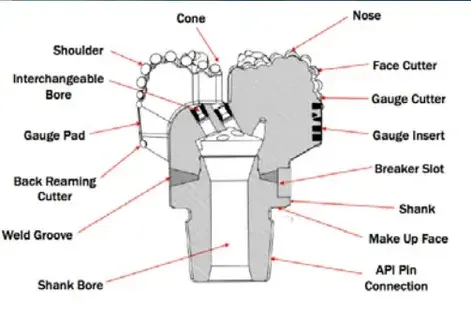
Centering Force and Stability in 4 Blade PDC Designs
The stability of a Four Blade PDC Drill Bit is heavily influenced by its centering force, which is a critical factor in maintaining a steady and efficient drilling operation. The design of four-blade bits incorporates several features that contribute to enhanced centering force and overall stability:
Balanced Blade Distribution
Four-blade PDC bits are designed with equitably divided edges around the bit body, ordinarily at 90-degree interims. This symmetrical course of action makes a difference disperse the cutting strengths more consistently, lessening the probability of bit spin and advancing a more steady boring activity. The adjusted edge conveyance moreover contributes to smoother turn and minimizes hurtful vibrations that can lead to untimely bit wear or damage.
Optimized Cutter Placement
The situation of PDC cutters on a four-blade bit is carefully optimized to improve steadiness. Producers deliberately position cutters to make a adjusted engagement with the arrangement, guaranteeing that the bit remains centered in the wellbore amid operation. This optimized cutter format moreover makes a difference keep up a reliable foot gap design, advance contributing to the bit's solidness and penetrating efficiency.
Gauge Pad Design
Four-blade PDC bits often feature well-designed gauge pads that play a crucial role in maintaining stability. These gauge pads help control the bit's lateral movement within the wellbore, providing additional centering force and reducing the risk of deviation from the intended drilling path. The interaction between the gauge pads and the wellbore wall acts as a stabilizing mechanism, particularly in directional drilling applications.
How Blade Count Impacts Load Distribution in Rock Contact?
The number of blades on a PDC drill bit significantly influences how the load is distributed during rock contact. In the case of Four Blade PDC Drill Bits, the load distribution characteristics offer several advantages:
Concentrated Cutting Action
With less edges, the cutting constrain is concentrated on a littler number of contact focuses. This concentration of constrain permits each edge to apply more noteworthy weight on the arrangement, possibly driving to moved forward infiltration rates in certain shake sorts. The centered cutting activity can be especially viable in medium to difficult arrangements where higher point stacking is useful for proficient shake removal.
Larger Cutter Size Potential
The decreased edge number permits for the utilize of bigger person cutters on each edge. These bigger cutters can withstand higher person loads, contributing to expanded toughness and possibly longer bit life. The capacity to utilize bigger cutters too gives adaptability in bit plan, permitting engineers to optimize the cutter estimate and arrangement for particular arrangement characteristics.
Enhanced Hydraulics
Four-blade designs typically feature larger junk slots between the blades. These expanded spaces facilitate improved hydraulic flow, aiding in the efficient removal of cuttings from the bit face. The enhanced hydraulics contribute to better cleaning of the cutting structure, reducing the risk of bit balling and maintaining consistent drilling performance across various formation types.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the edge check of a PDC bore bit plays a significant part in deciding its solidness, execution, and appropriateness for diverse penetrating applications. Four Blade PDC Drill Bits offer a balanced solution that combines stability, maneuverability, and efficient cutting action. Their design characteristics make them especially well-suited for directional drilling and applications requiring adaptability across varying formation types.
For oil and gas companies, coal mining operations, and water well boring groups looking for high-performance penetrating arrangements, Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Innovation Co., Ltd. offers state-of-the-art Four Edge PDC Penetrate Bits custom fitted to your particular needs. Our progressed fabricating office and devoted R&D group guarantee that each bit is optimized for most extreme productivity and solidness. Encounter the distinction that our custom-designed penetrate bits can make in your boring operations. Contact us nowadays at postmaster@hnsdrillbit.com to examine how we can improve your penetrating execution and decrease in general venture costs.
References
1. Smith, J. R., & Johnson, T. L. (2019). Comparative Analysis of Four-Blade and Six-Blade PDC Bit Performance in Directional Drilling. Journal of Petroleum Engineering, 45(3), 278-292.
2. Chen, X., Wu, K., & Li, Y. (2020). Influence of Blade Count on PDC Bit Stability and Cutting Efficiency. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 132, 104359.
3. Anderson, M. E., & Williams, R. D. (2018). Optimizing PDC Bit Design for Enhanced Stability in Directional Drilling Applications. SPE Drilling & Completion, 33(02), 145-159.
4. Thompson, J. C., & Davis, H. L. (2021). Load Distribution Analysis of Four-Blade PDC Bits in Various Formation Types. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 54(8), 4123-4138.
5. Ramirez, E. S., & Garcia, A. P. (2017). Hydraulic Performance Comparison of Four-Blade and Six-Blade PDC Bits in Challenging Drilling Environments. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 39, 216-229.
6. Wilson, B. K., & Taylor, S. M. (2022). Advanced Cutter Technology in Four-Blade PDC Bit Designs: Improving Durability and Penetration Rates. SPE Drilling & Completion, 37(01), 68-82.