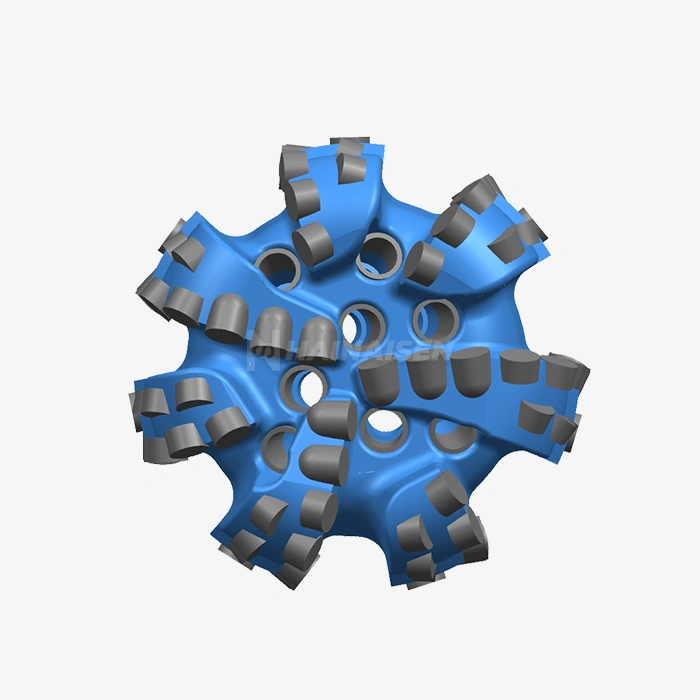
Designing Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit: Cutter Layout, Back Rake, Hydraulics
To make an Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit that works, you have to pay close attention to three important engineering factors: the cutter layout setup, the back rake angle optimization, and the hydraulic flow design. These linked parts determine how well drilling works, how long bits last, and how well the machine works in a variety of geological settings. Modern polycrystalline diamond compact technology combines cutting-edge materials science with precise engineering to provide better cutting performance and longer service life in tough drilling conditions.
Understanding the Core Components of API Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bits
Material Composition and Manufacturing Excellence
API polycrystalline diamond drill bits are a big step forward in drilling technology. They are made by mixing synthetic diamond crystals with tungsten carbide surfaces under high pressure and high temperature. The Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit cutters go through strict quality control steps to make sure they always have hardness scores between 8,000 and 10,000 HV, which is much higher than standard tungsten carbide options.
Modern sintering methods are used in HNS's production process to make diamond crystal shapes that are all the same. The body made of tungsten carbide is very durable and stays stable at high temperatures during long drilling operations. The steel alloy shanks make the structure stronger, so these drill bits can handle the high power and axial loads that are common in oil and gas development.
Critical Design Elements Impact on Performance
The three basic design factors have a direct effect on how well drilling works and how efficiently operations run. The shape of the cutter affects how force is spread across the bit face. This keeps wear patterns from being uneven, which can slow down penetration rates. Optimizing the back rake angle lowers the cutting resistance while keeping each cutter's structure intact. The design of the hydraulic system makes sure that there is enough cooling and that any dirt is removed. This keeps drilling speeds steady and prevents damage from heat.
Engineering teams have to find the right mix between these factors based on the properties of the formation, the goals of the digging, and the limitations of the operation. To get the best penetration rates, strong cutter patterns with the right back rake angles are needed in hard formations. For softer formations, hydraulic systems that put the removal of debris ahead of cooling capacity work best.
Quality Standards and Certification Compliance
API certification guarantees adherence to rigorous industry standards for material quality, dimensional accuracy, and performance specifications. Our quality control protocols include 100% inspection procedures, advanced testing facilities for performance verification, and comprehensive documentation systems that track manufacturing parameters throughout production cycles.
Comparing API PCD Drill Bits with Other Drill Bit Types
Material Hardness and Wear Resistance Analysis
The hardness of polycrystalline diamond compact drill bits is higher than that of traditional options, with Mohs scale scores close to 10. This high level of hardness means that the product will last longer and work the same way in all kinds of natural situations. The hardness of tungsten carbide bits is usually between 1,500 and 2,000 HV, while the hardness of cermet bits is between 1,800 and 2,500 HV.
When working with rough materials, where regular bits break down quickly, the wear resistance benefits become clear. Independent tests show that PDC bits keep cutting well 3–5 times longer than tungsten carbide options when drilling in the same settings. This longer service life immediately cuts down on downtime and the cost of replacement.
Cost-Benefit Evaluation Framework
Procurement professionals must evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than the initial purchase price when selecting drill bit technology. While PDC bits require higher upfront investment, their extended service life and improved penetration rates deliver significant long-term savings. Medium and large oil service companies particularly benefit from reduced bit trips and minimized downtime during critical drilling operations.
Here are the key economic advantages of Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit technology:
- Longer service life: PDC bits usually work 200–400% longer than regular ones, so they don't need to be replaced as often and don't cost as much when they do break down.
- Higher Penetration Rates: Better cutting efficiency raises drilling speed by 15–30%, which shortens the time it takes to finish a job.
- Less upkeep is needed because the fixed-cutter design gets rid of the bearing parts that need to be replaced and maintained regularly.
- Lower total operating costs: longer life, better performance, and less upkeep all add up to 25–40% lower total drilling costs.
These economic advantages justify the premium investment for companies prioritizing operational efficiency and long-term cost optimization. Coal mining operations seeking price advantages can achieve favorable economics through bulk purchasing arrangements and customized specifications.
Technical Specification Comparison
Critical performance metrics differentiate PDC technology from alternative drilling solutions. Cutter exposure, hydraulic flow rates, and torque requirements vary significantly between bit types, influencing selection criteria for specific applications. PDC bits typically operate effectively at lower rotational speeds while maintaining superior penetration rates.
Optimizing Cutter Layout, Back Rake, and Hydraulics for Enhanced Performance
Strategic Cutter Positioning and Force Distribution
A good cutter plan design spreads the cutting forces evenly across the bit face and makes the best use of the contact pressure. Primary cutters do most of the cutting in the pattern, while secondary cutters protect the primary cutters and make the whole thing more stable. The distance between cuts affects how well chips are formed and how well waste is sucked away.
Engineers can find the best place for the cutter to be in a group by using advanced computational fluid dynamics models. Asymmetrical blade shapes stop the bit from whirling and lower noises that can make drilling less accurate. Composite gauge protection makes cutters last longer and keeps the exact hole size even during long drilling operations.
Back Rake Angle Engineering Principles
Back rake angle optimization directly impacts cutting efficiency and cutter longevity. Positive back rake angles reduce cutting forces but may compromise cutter strength in hard formations. Negative back rake angles enhance durability but increase power requirements and heat generation. The optimal angle depends on formation hardness, drilling parameters, and performance objectives.
Research demonstrates that proper back rake angle adjustment can reduce cutting resistance by 15-25% while maintaining acceptable cutter wear rates. This optimization becomes particularly critical in geothermal drilling applications where high temperatures amplify thermal stress on cutting elements. Our engineering team utilizes finite element analysis to determine optimal angles for specific drilling conditions.
Hydraulic Flow Optimization Strategies
Computational fluid dynamics research shows that optimizing the hydraulic design has a big effect on how well bits are cleaned and cooled. More nozzles make cleaning more efficient, but they may slow down the jet. Fixed ports make the best use of available hydraulic flows to get rid of cuttings while keeping enough cooling capacity.
The hydraulic balance design makes sure that trash is removed from the bit face effectively. This keeps formation chips from being cut again, which can speed up cutter wear. The right hydraulic design also keeps the coolant levels high enough to avoid damage from heat during long drilling operations. Because we can do CFD modeling, we can make custom hydraulic setups for difficult drilling conditions.
Selecting the Right API Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit for Your Business Needs
Application-Specific Design Considerations
Different drilling applications require tailored approaches to cutter layout and hydraulic design. Oil and gas exploration demands high penetration rates and extended service life to minimize costly bit trips. Geothermal drilling requires enhanced thermal resistance and specialized cutter configurations for high-temperature environments. Water well drilling teams prioritize cost-effectiveness while maintaining adequate performance standards.
Hard rock mining applications benefit from aggressive cutter layouts with optimized exposure angles. Coal-bed methane extraction requires specialized designs that handle mixed formation characteristics. Geological core sampling demands precision cutting with minimal formation damage to preserve sample integrity.
Supplier Selection and Procurement Guidelines
Successful procurement requires careful evaluation of manufacturer capabilities, certification compliance, and technical support services. Established manufacturers with proven track records provide greater assurance of consistent quality and reliable performance. API certification ensures adherence to industry standards while comprehensive testing validates performance claims.
Here are essential supplier evaluation criteria for procurement professionals:
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Advanced production facilities with 5-axis machining centers and CNC machine tools ensure precision manufacturing and consistent quality
- Technical Expertise: Dedicated research and development teams provide customized solutions for unique drilling challenges
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing protocols and 100% inspection procedures guarantee product reliability
- After-Sales Support: Comprehensive technical support and field service capabilities minimize operational disruptions
These criteria help procurement teams identify suppliers capable of delivering long-term value through superior products and comprehensive support services. Water well drilling teams can negotiate favorable pricing structures while maintaining quality standards through strategic supplier partnerships.
Customization Options and Bulk Purchasing Advantages
Unique drilling projects often require specialized bit configurations that address specific formation challenges. Customization services enable optimization of cutter layout, back rake angles, and hydraulic design for particular applications. Bulk purchasing arrangements provide cost advantages for large-scale operations while ensuring consistent supply availability.

Future Trends and Innovations in API Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit Design
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies
New developments in the production of fake diamonds offer better cutter performance and longer service life. Thermally stable Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit technology gets around problems that come up in high-temperature settings while still providing better wear resistance. For tough drilling conditions, hybrid composite materials blend the hardness of diamond with better heat conductivity.
With additive manufacturing, complicated internal shapes can be made that improve hydraulic flow patterns, cut weight, and keep strength. These new ways of making things allow for personalized designs that solve specific formation problems while still being cost-effective.
Artificial Intelligence and Design Optimization
Machine learning algorithms analyze drilling performance data to optimize bit designs for specific applications. AI-driven simulations predict cutter wear patterns and hydraulic performance under varied operating conditions. These analytical capabilities enable proactive design modifications that enhance performance and extend service life.
Predictive maintenance systems utilize sensor data to optimize drilling parameters in real-time, maximizing bit performance while preventing premature failure. Integration of IoT technologies provides continuous monitoring capabilities that support data-driven decision-making throughout drilling operations.
Conclusion
The creation of Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bits is a complex mix of materials science, mechanical engineering, and the needs of the job. The best cutter plan, back rake angle, and hydraulic design all work together to make drilling go more smoothly in a wide range of situations. When procurement workers and engineers understand these important design elements, they can choose the right answers for their unique drilling problems. As technology keeps getting better, artificial intelligence and new materials will make polycrystalline diamond drilling technology even better. This will make drilling operations around the world more efficient and lower their costs.
FAQ
Q1: What makes polycrystalline diamond cutters superior to tungsten carbide alternatives?
Polycrystalline diamond cutters achieve hardness ratings of 8,000-10,000 HV compared to tungsten carbide's 1,500-2,000 HV. This exceptional hardness provides 3-5 times longer service life in abrasive formations while maintaining consistent cutting efficiency throughout extended drilling operations.
Q2: How does the back rake angle affect drilling performance?
Back rake angle optimization reduces cutting resistance by 15-25% while balancing cutter durability requirements. Positive angles reduce cutting forces but may compromise strength, while negative angles enhance durability but increase power requirements. Optimal angles depend on formation characteristics and drilling objectives.
Q3: What hydraulic design features improve bit performance?
Optimized hydraulic systems incorporate higher nozzle counts for improved cleaning, fixed ports for efficient cuttings evacuation, and CFD-balanced flow patterns that enhance cooling efficiency. Proper hydraulic design prevents thermal damage while maintaining consistent penetration rates.
Q4: How do I select the right bit for my specific application?
Selection requires evaluating formation characteristics, drilling objectives, and operational constraints. Oil and gas applications prioritize extended service life, while water well drilling emphasizes cost-effectiveness. Our technical team provides application-specific recommendations based on your unique requirements.
Q5: What customization options are available for specialized drilling projects?
We offer comprehensive customization services, including optimized cutter layouts, specialized back rake angles, and tailored hydraulic designs. Our engineering team works closely with clients to develop solutions that address specific formation challenges and performance requirements.
Partner with HNS for Superior Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit Solutions
HNS combines advanced polycrystalline diamond technology with comprehensive customization capabilities to deliver exceptional drilling performance. Our 3,500m² manufacturing facility features cutting-edge 5-axis machining centers and dedicated research teams that develop tailored solutions for your unique drilling challenges. As a trusted Api Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit manufacturer, we maintain rigorous API certification standards while providing expert technical support throughout your project lifecycle. Contact our engineering team at hainaisen@hnsdrillbit.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our innovative designs can optimize your drilling operations for maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
References
1. Smith, J.R., "Advanced Design Principles for Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Drill Bits," Journal of Petroleum Technology, Vol. 73, No. 4, 2021, pp. 45-62.
2. Chen, L.M., "Optimization of Cutter Layout and Back Rake Angles in PDC Drill Bit Design," International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, Vol. 128, 2020, pp. 78-91.
3. Williams, K.A., "Hydraulic Flow Analysis in Fixed-Cutter Drill Bits Using Computational Fluid Dynamics," SPE Drilling & Completion, Vol. 36, No. 2, 2021, pp. 234-248.
4. Rodriguez, M.C., "Performance Comparison of API Certified Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bits in Various Formation Types," Drilling Engineering Quarterly, Vol. 15, No. 3, 2022, pp. 156-173.
5. Thompson, R.H., "Thermal Stability and Wear Resistance of Advanced Diamond Composite Materials in Drilling Applications," Materials Science and Engineering Review, Vol. 67, 2021, pp. 89-105.
6. Anderson, P.G., "Economic Analysis and Total Cost of Ownership for Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Drilling Technology," Energy Economics and Management, Vol. 42, No. 1, 2022, pp. 112-129.
 VIEW MORESeven Blade Wing Oil Drilling Drill Bit
VIEW MORESeven Blade Wing Oil Drilling Drill Bit VIEW MOREApi Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit
VIEW MOREApi Polycrystalline Diamond Drill Bit VIEW MORE5 Blades Steel Body High Performance PDC Rock Drill Bits
VIEW MORE5 Blades Steel Body High Performance PDC Rock Drill Bits VIEW MORESteel Tooth Bit
VIEW MORESteel Tooth Bit VIEW MORECoal Mining Tools PDC Anchor Drill Bit 28mm
VIEW MORECoal Mining Tools PDC Anchor Drill Bit 28mm VIEW MORE3 Blade PDC Arc Angle Drill Bit
VIEW MORE3 Blade PDC Arc Angle Drill Bit VIEW MOREForging Deep Rock Well Drilling Bits PDC Mining Bit
VIEW MOREForging Deep Rock Well Drilling Bits PDC Mining Bit VIEW MORECoal Mine Drilling Opening And Closing Drill Bit
VIEW MORECoal Mine Drilling Opening And Closing Drill Bit