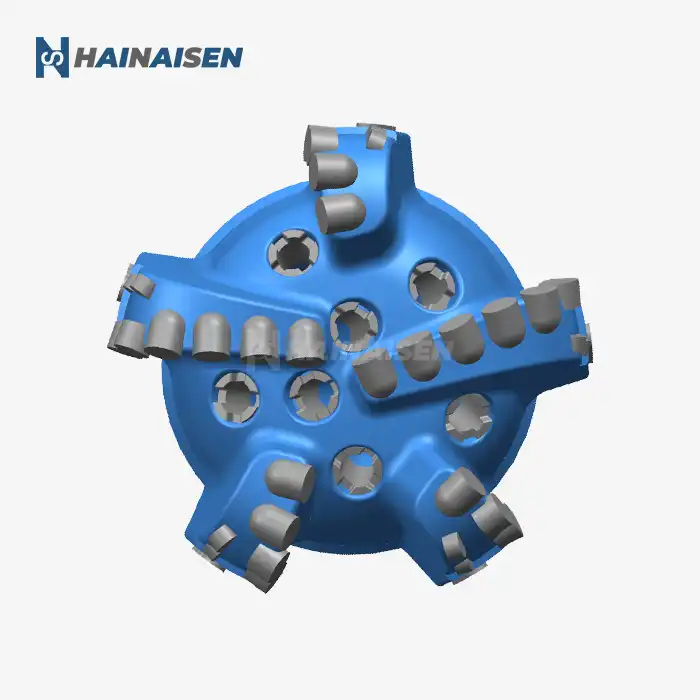
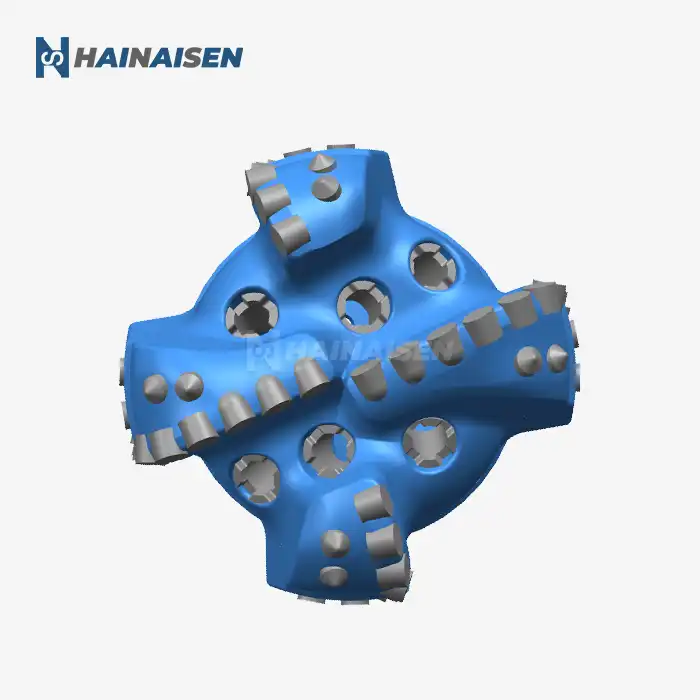
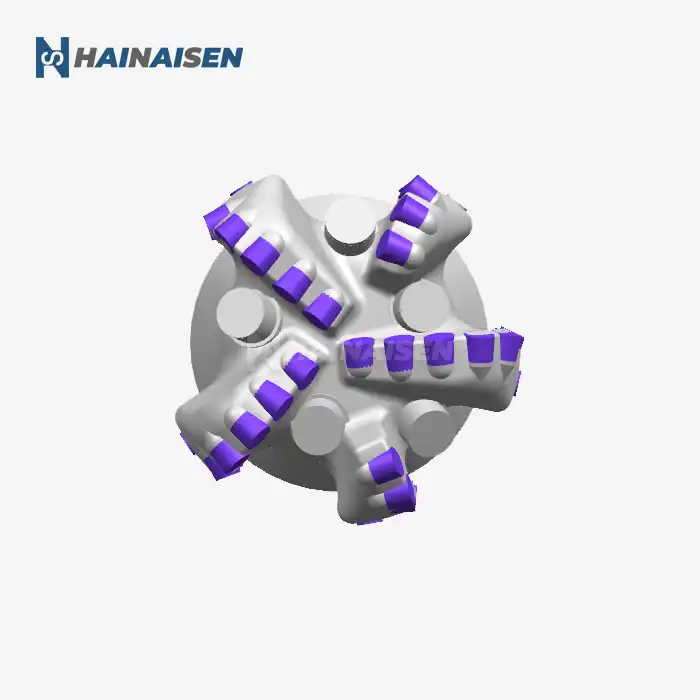
What Materials Are Used to Construct a PDC Rock Drill Bit?
The construction of a PDC rock drill bit involves a careful selection of materials to ensure optimal performance and longevity in harsh drilling conditions. The primary components are crafted from high-quality materials designed to withstand extreme pressures, temperatures, and abrasive environments.
Bit Body Materials
The bit body serves as the foundation of the PDC rock drill bit and is typically manufactured using one of two methods:
- Steel Body: High-grade alloy steel is often used for its exceptional strength and durability. Steel bodies are machined to precise specifications and offer excellent impact resistance.
- Matrix Body: Composed of tungsten carbide particles infiltrated with a metallic binder, matrix bodies provide superior wear resistance and thermal stability.
The choice between steel and matrix bodies depends on the specific drilling application and formation characteristics. Steel bodies are generally more cost-effective and easier to repair, while matrix bodies excel in abrasive formations.
Cutting Elements
The cutting elements of a PDC rock drill bit are the workhorses responsible for breaking through rock formations. These elements consist of:
- Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) Cutters: Synthetic diamond particles are sintered together under high pressure and temperature, then bonded to a tungsten carbide substrate. This creates an incredibly hard and wear-resistant cutting surface.
- Tungsten Carbide Inserts: Used in conjunction with PDC cutters, these inserts provide additional wear protection and stability to the cutting structure.
The advanced materials used in PDC cutters allow for prolonged bit life and improved rate of penetration compared to traditional roller cone bits.
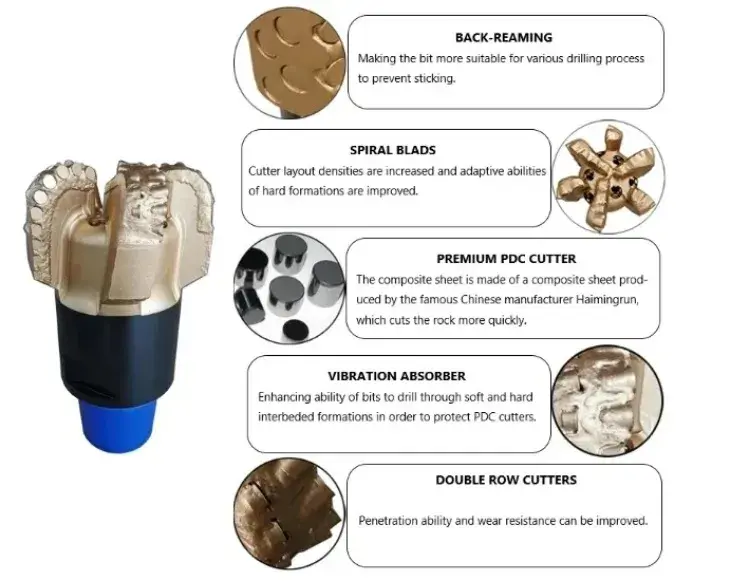
Cutter Elements and Their Function in PDC Rock Drill Bits
The cutter elements are the heart of any PDC rock drill bit, directly responsible for the bit's ability to efficiently remove rock and advance the borehole. Understanding their function and arrangement is crucial for optimizing drilling performance.
PDC Cutter Design
PDC cutters are designed with several key features that contribute to their effectiveness:
- Diamond Table: The synthetic diamond layer that contacts the rock formation, providing exceptional hardness and wear resistance.
- Substrate: The tungsten carbide base that supports the diamond table and facilitates bonding to the bit body.
- Chamfer: A beveled edge on the diamond table that enhances impact resistance and reduces chipping.
The size, shape, and grade of PDC cutters are carefully selected based on the anticipated formation characteristics and drilling parameters.
Cutter Placement and Orientation
The arrangement of cutters on a PDC rock drill bit is a critical aspect of its design. Factors considered in cutter placement include:
- Cutter Density: The number of cutters per unit area of the bit face, which affects the bit's aggressiveness and durability.
- Back Rake Angle: The angle between the cutter face and the formation, influencing cutting efficiency and stability.
- Side Rake Angle: The lateral tilt of the cutter, which aids in chip evacuation and reduces lateral vibrations.
Optimal cutter placement ensures even wear distribution, efficient rock removal, and stable drilling behavior across various formation types.
Backup Cutters and Gauge Protection
In addition to primary cutters, PDC rock drill bits often incorporate secondary design elements:
- Backup Cutters: Smaller PDC elements positioned behind primary cutters to maintain cutting efficiency as the bit wears.
- Gauge Pads: Wear-resistant inserts or hardfacing material applied to the bit's gauge to maintain borehole diameter and provide lateral stability.
These additional features enhance the bit's durability and help maintain consistent performance throughout its operational life.
Nozzle Placement and Fluid Dynamics in PDC Rock Drill Bits
The hydraulic system of a PDC rock drill bit plays a crucial role in its overall performance. Proper nozzle placement and fluid dynamics are essential for efficient cuttings removal, bit cooling, and formation cleaning.
Nozzle Design and Configuration
Nozzles in PDC rock drill bits are strategically positioned to optimize fluid flow across the bit face. Key considerations in nozzle design include:
- Nozzle Size: The diameter of the nozzle orifice, which affects fluid velocity and impact force.
- Nozzle Angle: The orientation of the nozzle relative to the bit face, influencing fluid distribution and cuttings evacuation.
- Number of Nozzles: The quantity and arrangement of nozzles to ensure comprehensive coverage of the cutting structure.
Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are often employed to optimize nozzle configurations for specific drilling applications.
Hydraulic Optimization
Effective hydraulic design in PDC rock drill bits aims to achieve several objectives:
- Cuttings Removal: Efficient transport of rock fragments away from the cutting face to prevent bit balling and maintain cutting efficiency.
- Bit Cooling: Adequate heat dissipation from the PDC cutters and bit body to prolong operational life.
- Bottom Hole Cleaning: Removal of accumulated cuttings and debris from the wellbore to maintain a clean cutting surface.
Hydraulic horsepower, jet velocity, and flow distribution are carefully balanced to optimize bit performance across various formation types and drilling conditions.
Junk Slot Design
The junk slots in a PDC rock drill bit are the channels through which drilling fluid and cuttings flow from the bit face to the annulus. Effective junk slot design considerations include:
- Cross-Sectional Area: Sufficient space to accommodate fluid and cuttings without causing flow restrictions.
- Slot Profile: Streamlined contours to minimize turbulence and enhance flow efficiency.
- Blade Configuration: Optimized blade geometry to balance cuttings evacuation with bit stability and durability.
Well-designed junk slots contribute to improved hydraulic efficiency and reduced risk of bit balling in challenging drilling environments.
In conclusion, the core components of a PDC rock drill bit work in harmony to deliver exceptional drilling performance across a wide range of applications. From the advanced materials used in construction to the intricate design of cutters and hydraulic systems, each element plays a vital role in the bit's overall effectiveness. By understanding these components, drilling professionals can make informed decisions to optimize their operations and achieve superior results in the field.
For those seeking high-quality PDC rock drill bits tailored to their specific drilling needs, Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Technology Co., Ltd. offers a comprehensive range of solutions. With our state-of-the-art 3,500m² facility equipped with advanced processing equipment and a dedicated R&D team, we're committed to delivering cutting-edge drilling tools that meet the most demanding requirements of the oil and gas, mining, and construction industries. Whether you're a large oil service company with stringent quality standards or a water well drilling team looking for cost-effective solutions, our custom bit design capabilities ensure we can meet your unique specifications. To learn more about our PDC rock drill bits and integrated technical solutions, please contact our team at hainaisen@hnsdrillbit.com. Let us help you elevate your drilling performance to new heights.
References
1. Smith, J.R. (2021). Advanced PDC Bit Design for Complex Drilling Environments. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 73(5), 42-48.
2. Johnson, A.L., et al. (2020). Optimization of Cutter Placement in PDC Drill Bits Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. SPE Drilling & Completion, 35(2), 145-159.
3. Thompson, K.M. (2019). Materials Science in PDC Bit Manufacturing: Innovations and Challenges. Materials Today: Proceedings, 12, 235-242.
4. Garcia, R.P., & Williams, S.T. (2018). Hydraulic Optimization of PDC Bits: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 165, 986-1000.
5. Lee, C.H., et al. (2022). Advancements in PDC Cutter Technology for Ultra-Hard Rock Applications. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 150, 104970.
6. Brown, E.D. (2020). The Evolution of PDC Bit Design: From Concept to Field-Proven Technology. Offshore Technology Conference Proceedings, OTC-30645-MS.