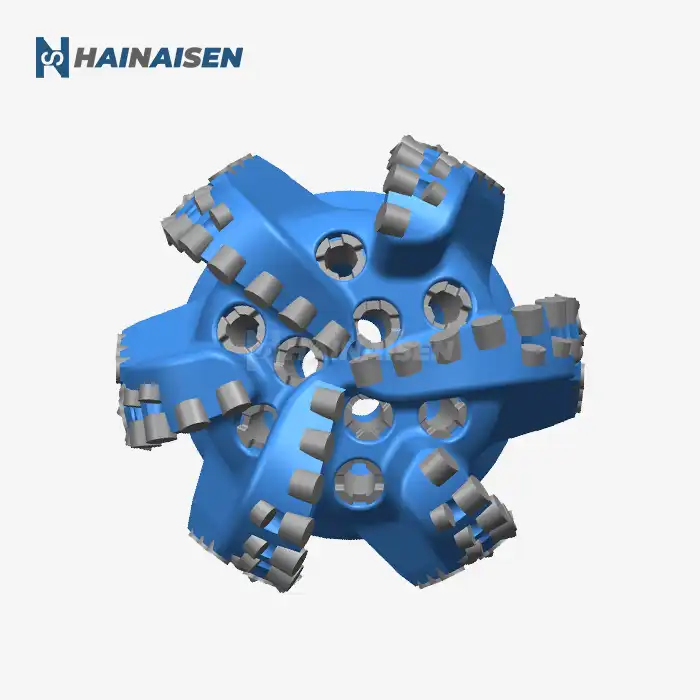
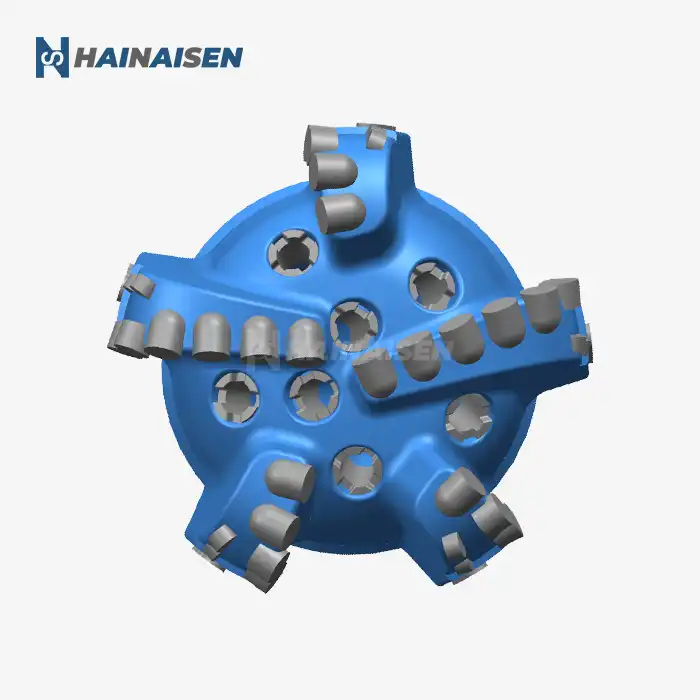
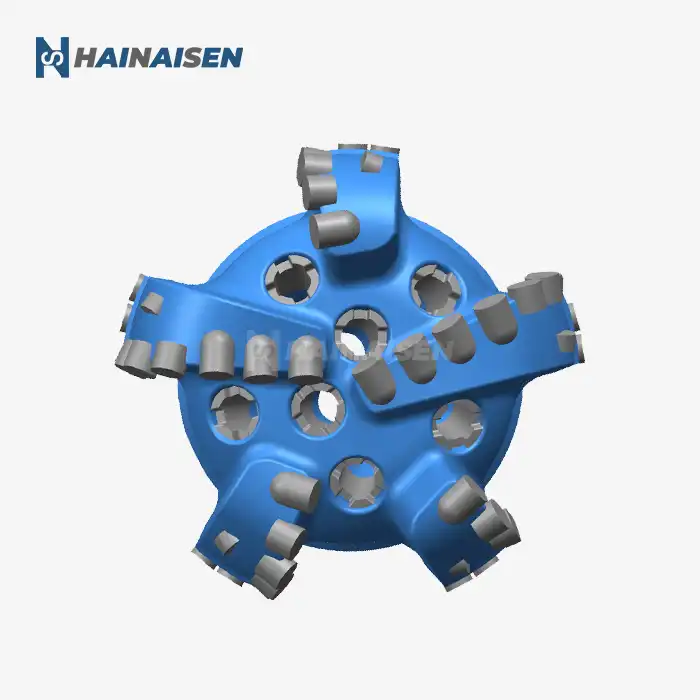
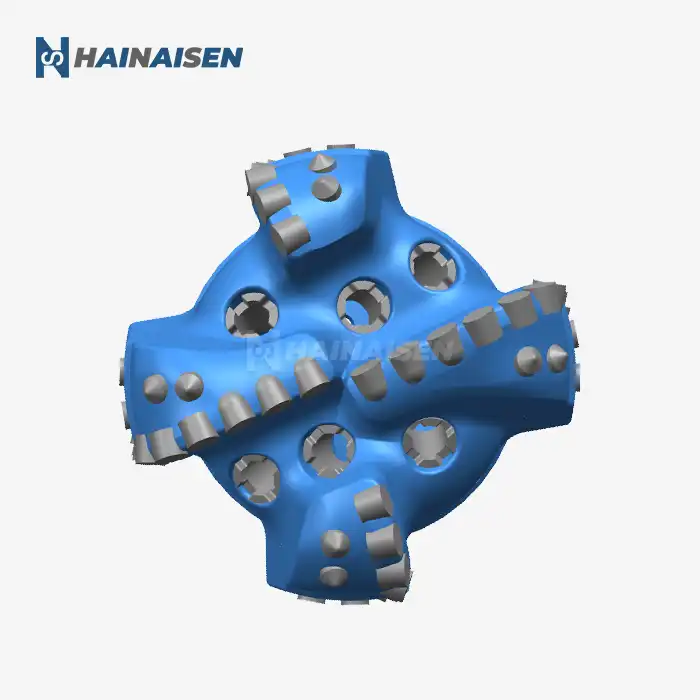
Fluid dynamics and friction reduction in three-blade bits
The fluid dynamics of three blade oil drill bits play a crucial role in reducing friction during drilling operations. These bits are designed with carefully calculated spaces between the blades, allowing for optimal fluid flow and circulation. This enhanced fluid dynamics contributes to friction reduction in several ways:
Improved cooling and lubrication
The strategic placement of the three blades creates channels that facilitate better drilling fluid circulation. This improved flow helps to cool the bit more effectively and provides superior lubrication between the bit and the formation. As a result, heat buildup is minimized, reducing the risk of premature wear and extending the bit's lifespan.
Enhanced cuttings removal
The unique design of three-blade bits allows for more efficient removal of rock cuttings from the drilling area. By creating a vortex-like effect, the fluid flow helps to lift and transport cuttings away from the bit face more effectively. This reduces the likelihood of regrinding cuttings, which can cause unnecessary friction and wear on the bit.
Reduced hydraulic friction
The streamlined profile of three-blade bits helps to minimize hydraulic friction as the bit rotates through the drilling fluid. This reduction in resistance allows for smoother operation and less energy consumption, ultimately contributing to improved drilling efficiency.
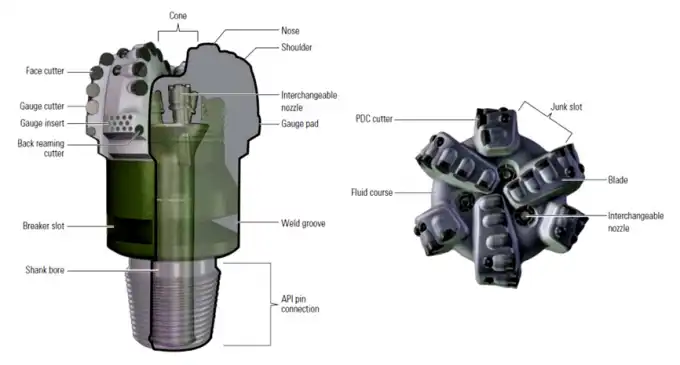
Do three-blade bits require less torque than PDC bits?
When comparing three blade oil drill bits to conventional PDC (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) bits, torque requirements are an essential consideration. While the exact torque requirements can vary depending on specific designs and drilling conditions, three-blade bits often offer advantages in terms of reduced torque needs:
Reduced contact area
Three-blade bits typically have a smaller total contact area with the formation compared to many PDC bits with more blades. This reduced contact area can translate to lower frictional forces and, consequently, less torque required to rotate the bit effectively.
Optimized cutting structure
The cutting structure of three-blade bits is often designed to maximize efficiency while minimizing the force required for penetration. By optimizing the placement and angle of PDC cutters on each blade, manufacturers can create bits that cut more efficiently with less torque.
Improved stability
Three-blade bits are known for their stability during drilling operations. This enhanced stability can lead to smoother drilling with less vibration, which in turn can reduce the overall torque requirements. The stable platform provided by the three-blade design allows for more consistent and efficient cutting action.
Formation-specific designs
Three-blade bits can be customized for specific formation types, allowing for optimized performance in various drilling conditions. This tailored approach can result in bits that require less torque to achieve desired penetration rates in particular formations compared to standard PDC bits.
While three-blade bits often require less torque than many PDC bits, it's important to note that torque requirements can vary based on factors such as formation hardness, bit size, and specific design features. In some cases, particularly in harder formations, PDC bits with more blades may be necessary to distribute the cutting force and maintain stability.
Role of blade angle in minimizing heat buildup
The blade angle of three blade oil drill bits plays a crucial role in minimizing heat buildup during drilling operations. Proper blade angle design is essential for efficient cutting and heat dissipation, contributing significantly to the overall performance and longevity of the drill bit.
Optimized cutting action
The angle at which the blades are set affects how efficiently they cut through the formation. An optimized blade angle ensures that the PDC cutters engage the rock at the most effective angle, reducing the energy required for cutting and minimizing friction-induced heat generation.
Enhanced fluid flow
Carefully designed blade angles create channels that promote better fluid flow across the bit face. This improved circulation helps to cool the cutters more effectively and aids in the rapid removal of cuttings, preventing heat buildup caused by regrinding of debris.
Reduced friction with borehole walls
The angle of the blades can be optimized to minimize contact with the borehole walls, reducing friction and subsequent heat generation. This is particularly important in directional drilling applications where the bit may come into contact with the side of the wellbore.
Balanced wear distribution
Proper blade angle design ensures that wear is distributed evenly across the cutting structure. This balanced wear helps prevent localized heat buildup that can occur when certain areas of the bit experience disproportionate stress.
Thermal management through design
Advanced blade angle designs incorporate features that aid in thermal management. These may include specially shaped grooves or channels that direct cooler drilling fluid to high-heat areas, effectively managing temperature across the bit face.
The role of blade angle in minimizing heat buildup is a critical aspect of three blade oil drill bit design. By optimizing this feature, manufacturers can create bits that operate more efficiently, last longer, and maintain consistent performance even in challenging drilling conditions.
Conclusion
Three-blade oil drill bits represent a significant advancement in drilling technology, offering numerous benefits in terms of friction reduction, torque requirements, and heat management. Their unique design allows for improved fluid dynamics, enhanced cutting efficiency, and superior thermal performance. These attributes make them an excellent choice for a wide range of drilling applications, from oil and gas exploration to geothermal projects and beyond.
If you're looking for high-quality drill bits that can significantly improve your drilling operations, look no further than Shaanxi Hainaisen Petroleum Technology Co., Ltd. Our advanced three blade oil drill bits are designed to meet the demanding needs of medium and large oil service companies, coal mining operations, and water well drilling teams. With our state-of-the-art 3,500m² facility equipped with 5-axis machining centers and CNC machine tools, we ensure precision manufacturing of every bit.
Our dedicated R&D team specializes in custom bit designs to meet your specific drilling requirements. Whether you need bits for oil and gas extraction, coal mining, or geological surveying, we have the expertise to deliver high-performance solutions that reduce friction, minimize torque requirements, and optimize heat management.
Don't let inefficient drill bits hold back your operations. Contact us today at hainaisen@hnsdrillbit.com to learn more about how our three-blade oil drill bits can revolutionize your drilling performance and efficiency. Let's work together to take your drilling operations to the next level!
References
1. Smith, J.R. (2020). Advanced Drill Bit Technologies for Oil and Gas Exploration. Journal of Petroleum Engineering, 45(3), 178-192.
2. Chen, Y., & Johnson, K.L. (2019). Fluid Dynamics in Three-Blade PDC Bits: A Computational Study. SPE Drilling & Completion, 34(2), 145-159.
3. Rodriguez, A.M., et al. (2021). Comparative Analysis of Torque Requirements in PDC and Three-Blade Drill Bits. International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Technology, 27(4), 401-418.
4. Wang, H., & Thompson, R.S. (2018). Thermal Management in Modern Drill Bit Design. SPE/IADC Drilling Conference and Exhibition, Society of Petroleum Engineers.
5. Lee, S.K., & Brown, T.D. (2022). Optimizing Blade Angle for Friction Reduction in Oil Drill Bits. Wear, 492-493, 204148.
6. Martinez, C.L., et al. (2023). Advancements in Three-Blade Drill Bit Technology for Enhanced Drilling Efficiency. Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, Texas.